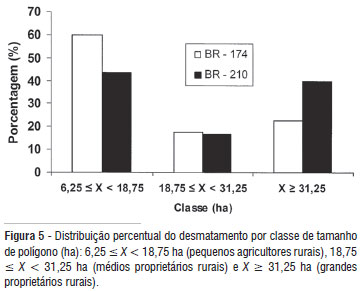
Deforestation in the Amazon currently represents one of the greatest environmental issues in Brazil, and stopping this process requires public policies based on understanding the forces that control the forest loss in different parts of Amazonia. We evaluated deforestation in the southern portion of Roraima State using a Geographical Information System (GIS) to delineate buffers along each of the two main highways that cross the region: BR-174 and BR-210. Each buffer was 20 km wide and was divided into eight strips 2500 m in width. The study covered the 2001-2007 period using annual deforestation data from PRODES vector files and visual analysis of TM Landsat 5 imagery. We also used shape files of roads and settlement projects in the southern part of Roraima coupled with field observations. Deforestation in the period was strongly related to the availability of roads and to the number of families present in the settlement project. The occurrence of deforestation was highest in the area of the BR-210 where large landowners and land invasions were present. The logging center on the BR-174 may have influenced the formation of small clearings in the Rorainópolis city neighbor. Predatory logging and new land occupations by both small and large landholders are spreading quickly in a disorderly fashion. This situation has high potential for forest loss since migration is expected to increase if Roraima is connected to the "Arc of Deforestation" by reopening the BR-319 Highway, which would connect Manaus to Porto Velho.
Amazon; Logging; Illegal Occupation of Lands; Geographic Information System