ABSTRACT
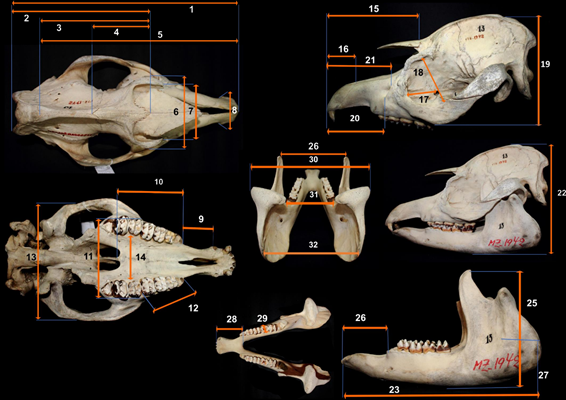
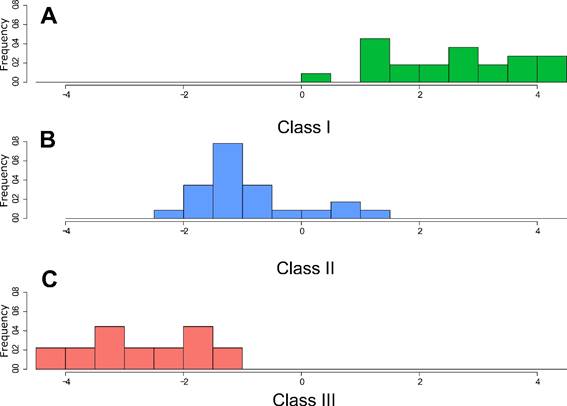
The skulls of 54 specimens of the South American tapir, Tapirus terrestris collected in the department of Loreto, Peru were measured, analyzed and compared to investigate skull development of this species. Univariate, multivariate and allometric analyses were performed using 32 skull variables through traditional morphometrics. Significant skull shape variation was detected among ontogenetic classes. Young individuals (class I, n = 22) showed higher variation than subadults and adults (class II, n = 23 and class III, n = 9), without evidence of sexual dimorphism (males = 35, females = 19). Principal component analyses and discriminant function analysis showed almost complete separation of the age classes. Allometric analysis indicated a tendency of unproportioned cranial growth. All our samples come from the same population living under the same ecological condition, which eliminates the effect of confounding variables related to habitat on the pattern of ontogenetic variation of this anatomical structure.
KEYWORDS:
Amazonia; morphology; skull; tapir, ontogeny

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail