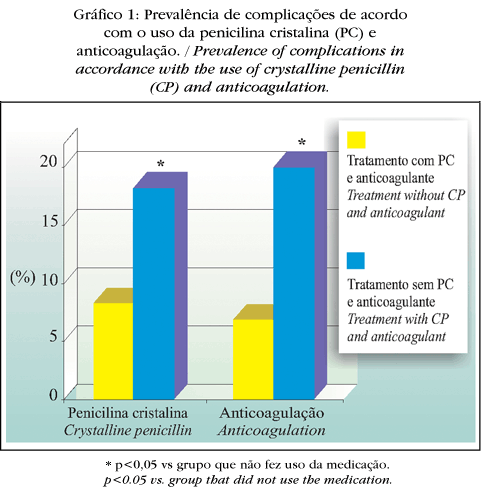
BACKGROUND: Erysipelas and cellulitis are common skin infections. OBJECTIVES: The aim of this paper is to investigate the frequency, risk factors, clinical features, complications, principal drugs used for treatment and the disease course. METHODS: The authors studied 35 ward patients who had been diagnosed with erysipelas, and were admitted to the Central Hospital of Irmandade da Santa Casa de Misericórdia de São Paulo between April and August 2002. RESULTS: Among the patients in the ward during the study 0.87% had been diagnosed with erysipelas. The most common local risk factor was lymphedema, followed by previous episodes of erysipelas. Among the general risk factors, diabetes mellitus, alcohol abuse and cancer were most frequently observed. Local inflammatory signs were found in 97.8% of the patients. Four cases were observed to have complications, which were: necrosis, abscess, deep thrombophlebitis and septicemia. The course was satisfactory in more than 97% of patients. CONCLUSIONS: Therapy with penicillin was associated with a decrease of complications (p<0.05) and at a lower cost compared to other antibiotic therapies (p<0.05). When anticoagulants were combined to the therapy, there was a lower incidence of complications (p<0.05).
cellulitis; erysipelas; heparin; therapeutic