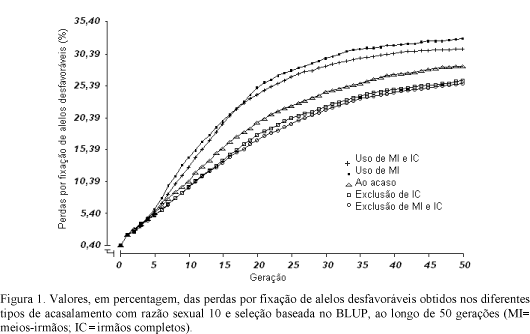
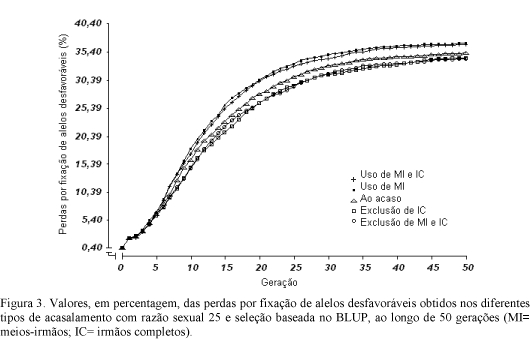
Populations of five different mating designs, submitted to selection based on best linear unbiased predicto (BLUP)r, were evaluated regarding to genetic losses by fixation of unfavorable alleles and selection limit, during 50 generations. Simulated data were used to obtain the genome of all individuals of the populations. A quantitative trait with heritability of 0.10 was studied in the selected populations, with the following structure: sexual ratio of 10, 20, 25, and 50 and effective population size of 36.36, 19.05, 15.38 and 7.84, respectively. For each sexual ratio different populations were generated corresponding to the following mating designs: preferential matings between half and full sibs, preferential matings between half sibs, random matings, exclusion of matings between full sibs and exclusion of matings of half and full sibs. Smallest percentage of unfavorably fixed loci and the highest selection limit were observed in the lower sexual ratio (d= 10). Better differentiation between the studied mating designs was also observed for the lower sexual ratio.
genetic loss; unfavorable allele; sexual ratio; selection limit; effective size