ABSTRACT
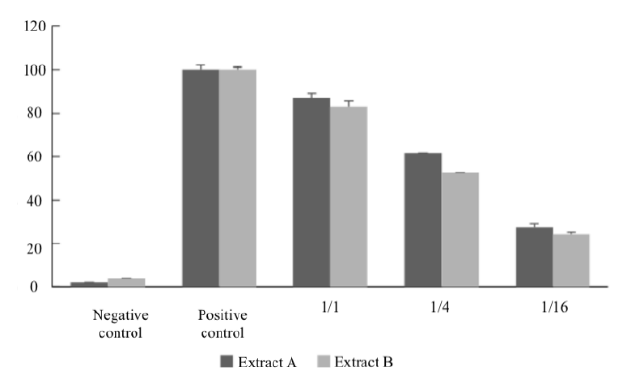
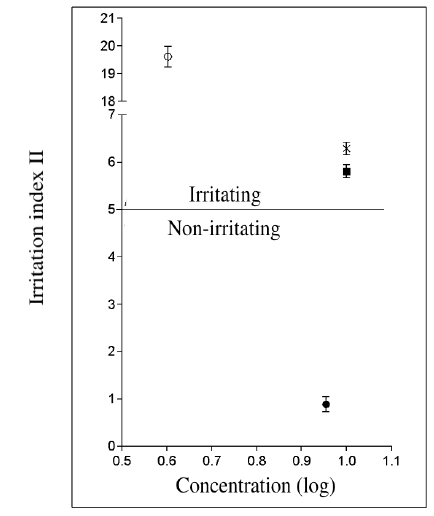
Ateleia glazioviana is an important poisonous plant in southern Brazil, responsible for important economic losses in livestock. The aim of this work was to identify the amount of potential toxic active components in different vegetative stages. Plant samples were collected at different maturity stages and identified for registration in the SISGEN system. An aqueous extract was obtained from the leaves to evaluate the predominant compounds present in the samples (200g/500mL). Chemical detection of toxic compounds was performed using gas chromatography. Subsequently, the most expressive chemical groups were analyzed and compared with structures of toxic potential, with phenolic/ketonic groups being found (spectral region between 4,600 and 4,700cm-1), suggesting substances already identified as Glaziovianin A or Rotenone. The amount of toxic compound in fresh plant was determined to be 0.0013mg/kg. There was no difference in the quantity of the toxic compound in relation to the maturity degree of the plant or season. The results of toxicological tests for the degree of irritation and cellular damage were positive. Due to the structural similarities of these molecules, further analyses are necessary to characterize the compounds more accurately.
Keywords:
gas chromatography; poisonous plant; ruminant; toxicology

 Physicochemical characterization of different vegetative stages of Ateleia glazioviana
Physicochemical characterization of different vegetative stages of Ateleia glazioviana Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail

 Source: Yokosuka et al., 2017.
Source: Yokosuka et al., 2017.