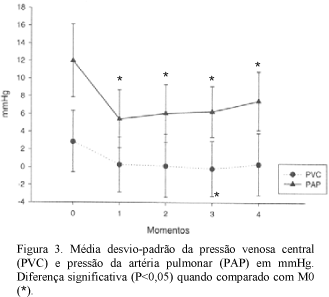
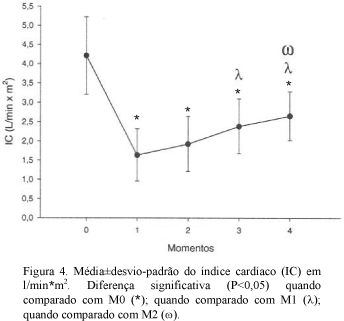
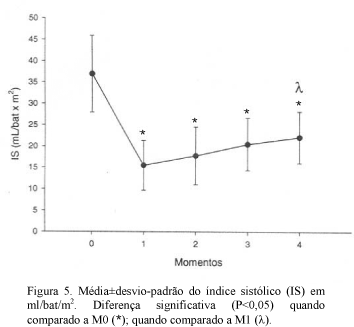
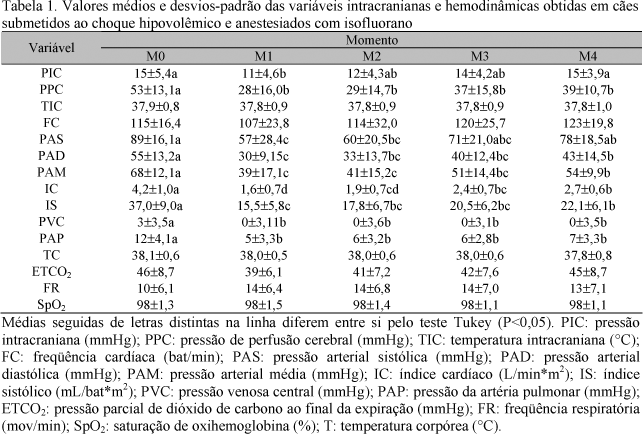
Intracranial and hemodynamic alterations in 20 adult dogs anesthetized with isoflurane and submitted to acute hemorrhage were studied. Anesthetic influence on cerebral auto-regulation mechanism was also observed. General anesthesia was induced with at 3.5V% (volume %) isoflurane. Thereafter, orotracheal intubation was performed and vaporizer was calibrated to 2.1V%. To induce hypovolemia, a total amount of 35 ml/kg-1 of blood was taken from each dog. Intracranial pressure (ICP); intracranial (ICT) and body temperatures (BT); cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP); systolic (SAP), diastolic (DAP) and mean arterial pressures (MAP); heart (HR) and respiratory rates (RR); cardiac (CI) and stroke indexes (SI); central venous pressure (CVP); pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP); end tidal dioxide carbon (ETCO2); and oxyhemoglobin saturation (SpO2) were evaluated. Immediately after hypovolemia, there was significative reduction of ICP, CPP, SAP, DAP, MAP, CI, SI, and PAP. Ten minutes after, the values increased gradually until the end of the experimental period. Indeed, acute hemorrhage caused reduction of hemodynamic variables and activation of the compensatory mechanisms. Cerebral blood perfusion was reduced and cerebral auto-regulation mechanism was activated due to hypovolemia associated to isoflurane anesthesia.
dog; hypovolemia; isoflurane; cerebral auto-regulation; hemodynamic