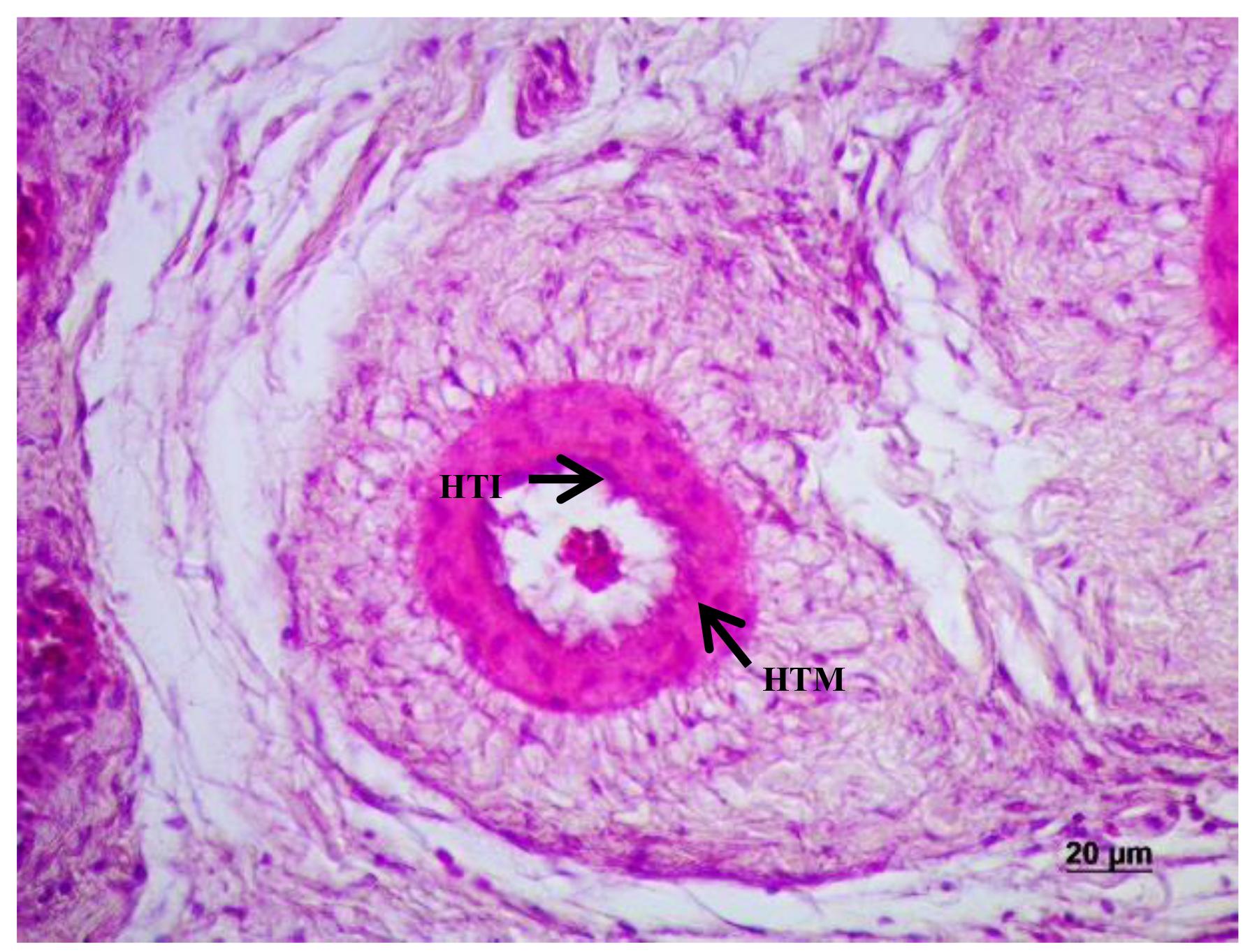
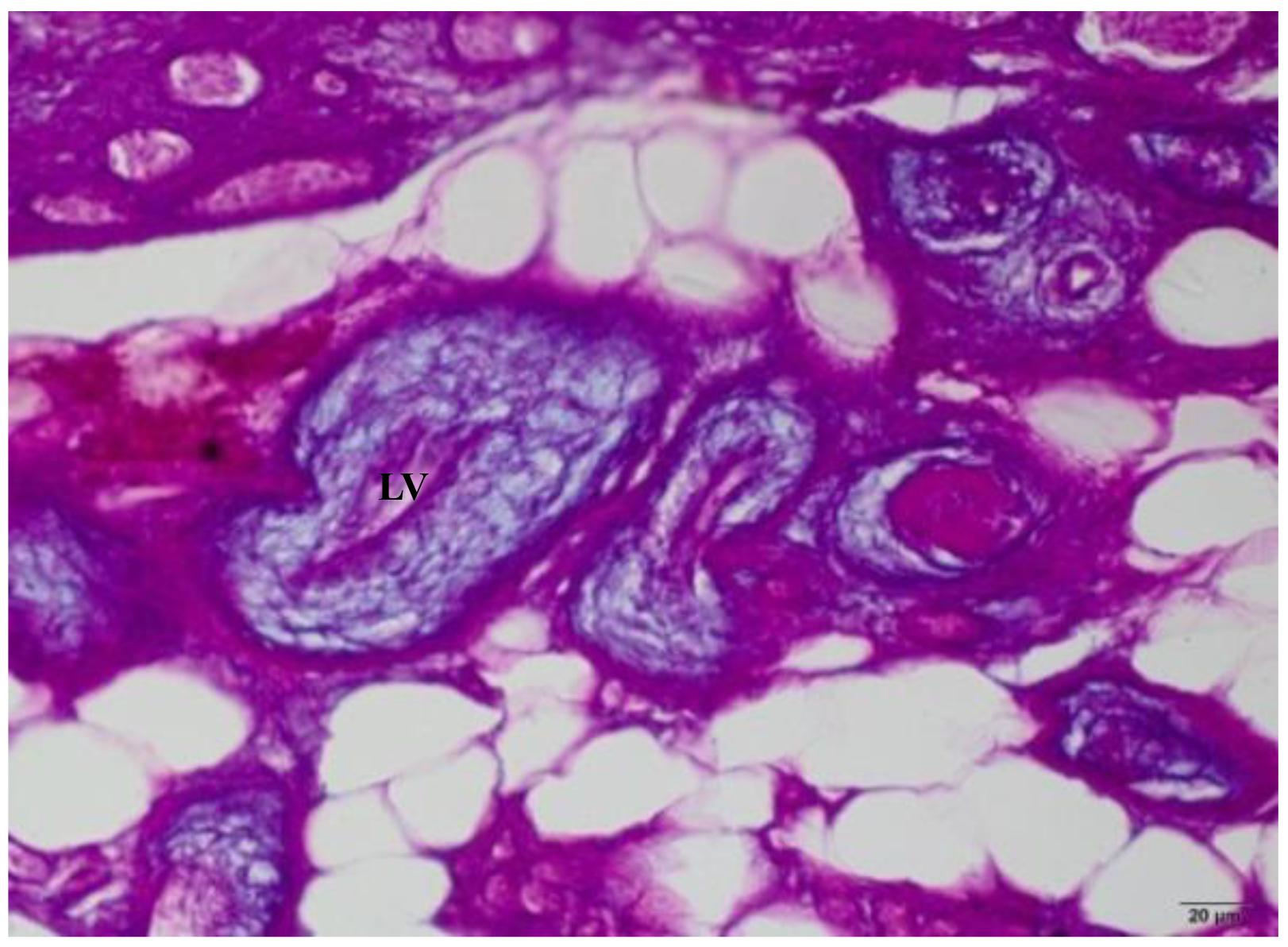
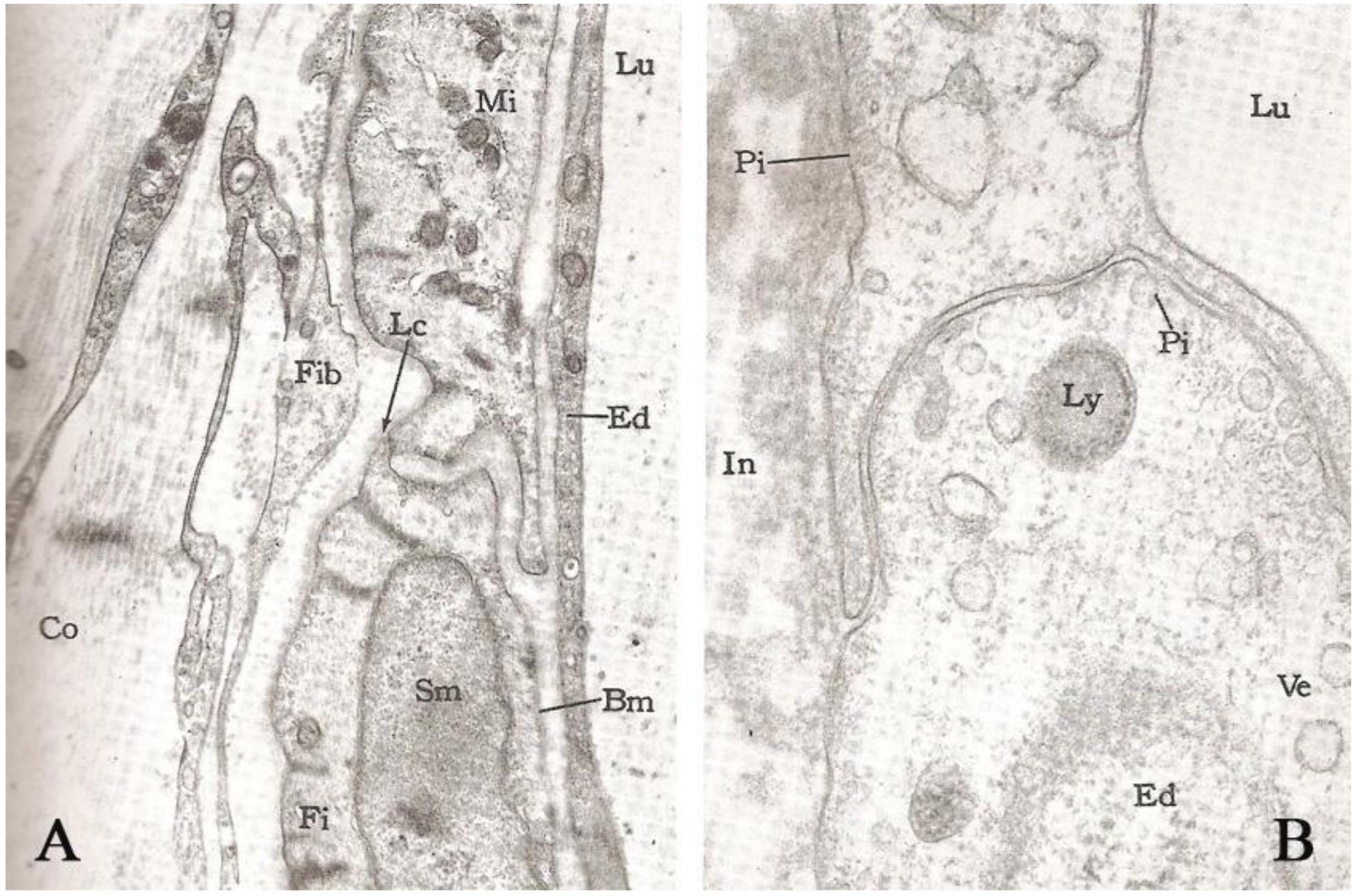
The coronary lesions have been reported in species of anadromous fish with similar characteristics as those observed in human atherosclerosis, but not in farmed fish without interference of reproductive patterns. This study aimed to describe coronary lesions in beijupirá (Rachycentron canadum) farmed in an offshore system, in 54 specimens collected along an eight month cultivation period. Samples of heart tissue of fry and juveniles were subjected to histopathological analysis and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for visualization of coronary lesions, the histology slides were stained using hematoxylin-eosin, periodic acid Schiffh, alcian blue, and reticulin of Gomori. Examinations performed by light microscopy showed arterial lesions characterized by hyperplasia of the intima and media tunics, respectively in 29.63% and 79.63 % of the animals, with reduced lumen. In TEM changes in the structure of the coronary endothelium and thickening of the basement membrane, proliferation of fibroblasts and collagen fibers, with subendothelial accumulation of lipid material, cellular debris adhering to the basement membrane and presence of pinocytotics vesicles and isolated lysosomes were observed. It has been found that the Rachycentron canadum fish species farmed in captivity develop arterial lesion of the chronic inflammatory degenerative type.
atherosclerosis; hyperplasia; histopathology; transmission electron microscopy; Rachycentron canadum

 Hyperplasia in tunics of coronary arteries in beijupirá farmed in
offshore system
Hyperplasia in tunics of coronary arteries in beijupirá farmed in
offshore system