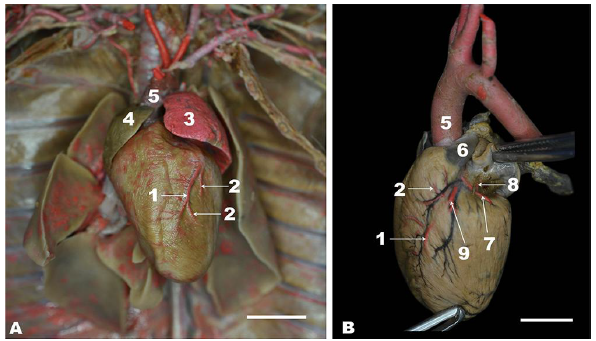
Figure 1
Topographical location of the opossum heart through opened intercostal spaces (A) and ventral view of the heart in situ (B) of the white-eared opossum. 1, cranial lobe of the right lung; 2, middle lobe of the right lung; 3, caudal lobe of the right lung; 4, cranial lobe of the left lung; 5, caudal lobe of left lung; 6, accessory lobe of right lung; 7, caudal vena cava; 8, pericardium; 9, phrenicopericardiac ligament; r1, first rib; r13, last rib (13th rib); is2nd, second intercostal space; is3rd, third intercostal space; is4th, fourth intercostal space; is5th, fifth intercostal space. Bar=1 cm.
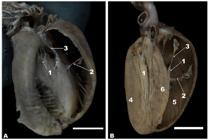
Figure 2
Auricular (A) and atrial (B) surfaces of the white-eared opossum heart. 1, right auricle; 2, right ventricle; 3, left auricle; 4, left ventricle; 5, paraconal interventricular groove; 6, conus arteriosus; 7, pulmonary trunk; 8, aortic arch; 9, thoracic aorta; 10, brachiocephalic trunk; 11, right subclavian artery; 12, bicarotid trunk; 13, left subclavian artery; 14, right common carotid artery; 15, left common carotid artery; 16, left atrium; 17, right atrium; 18, cranial vena cava; 19, caudal vena cava; 20, subsinuosal interventricular groove. Bar=1 cm.
Figure 3
Cranioventral view of isolated white-eared opossum heart and lungs. 1, right atrium; 2, right ventricle; 3, left ventricle; 4, conus arteriosus; 5, pulmonary trunk; 6, ascending aorta; 7, left phrenic nerve; 8, brachiocephalic trunk; 9, right subclavian artery; 10, bicarotid trunk; 11, right subclavian artery; 12, left common carotid artery; 13, right common carotid artery; 14, right phrenic nerve; 15, trachea; 16, cranial vena cava; 17, cranial lobe of right lung; 18, middle lobe of right lung; 19, caudal lobe of right lung; 20, accessory lobe of right lung; 21, caudal vena cava; 22, cranial lobe of left lung; 23, caudal lobe of left lung. Bar=1cm.
Figure 4
Internal view of the dorsum of the opened right atrium (A and B). Internal view of the dorsum of the opened right and left atria (C). 1, pectinate muscles; 2, ostium of the caudal vena cava; 3, ostium of the cranial vena cava; 4, cavity of the right auricle; 5, intervenous tubercle; 6, oval fossa; 7, interatrial septum; 8, pulmonary trunk; 9, aorta; LA, left atrium; RA, right atrium. Bar=1cm.
Figure 5
Internal view of the right (A) ventricle and right and left cardiac ventricles (B) in the white-eared opossum heart. 1, papillary muscles; 2, right septomarginal trabecula; 3, chordae tendineae; 4, free wall of left ventricle (myocardium); 5, right ventricle; 6, interventricular septum. Bar=1cm.
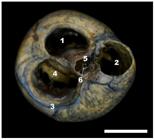
Figure 6
Dorsal view of white-eared opossum heart with atria removed. 1, left atrioventricular ostium; 2, pulmonary trunk ostium; 3, right atrioventricular ostium with right coronary artery; 4, right atrioventricular valve (septal cusp); 5, aortic ostium; 6, aortic valve. Bar=1cm.
Figure 7
Auricular surface (A) and left ventricular margin of the auricular surface (B) of the white-eared opossum heart with latex injected into coronary vessels. 1, paraconal interventricular branch; 2, ventricular branches; 3, left auricle; 4, right auricle; 5, ascending aorta; 6, pulmonary trunk; 7, circumflex branch; 8, atrial branch; 9, ventricular branch. Bar=1cm.
Figure 8
Atrial surface of the white-eared opossum heart with latex injected into coronary vessels: right atrium and auricle retracted with forceps. 1, right coronary artery; 2, ventricular branches; 3, right marginal branch; 4, subsinuosal interventricular branch; 5, conus arteriosus; 6, ascending aorta; 7, right atrium (retracted with forceps); 8, atrial branch; 9, right lung. Bar=1cm.
Figure 9
Atrial view of white-eared opossum heart with epoxy injected into coronary vessels and microvasculature (A,B,C). 1, subsinuosal interventricular branch; 2, ventricular branches; 3, right coronary artery; 4, right coronary artery arising from the aortic bulb; 5, ascending aorta; 6, right marginal branch; 7, paraconal interventricular branch. Bar=1cm.

 Anatomy of the heart and coronary blood supply of the white-eared opossum (Didelphis albiventris)
Anatomy of the heart and coronary blood supply of the white-eared opossum (Didelphis albiventris)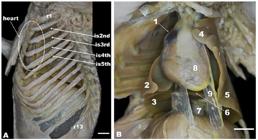 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail