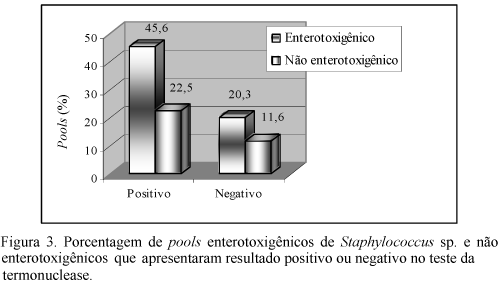
In order to count and identify Staphylococcus sp., the detection of the Staphylococcal enterotoxins (SE) and toxic shock toxin syndrome (TSST-1), 80 raw milk samples cooled at 4°C and stored in bulk tanks for 48 hours in different farms from Minas Gerais State were analyzed. Staphylococcus sp. was observed in all samples and the counts varied from 1.0 × 10(5) to 2.5 × 10(7) CFU/ml (mean = 5.60 log CFU/ml; sd = 0.53 and CV = 9.46 %). A total of 436 strains of Staphylococcus were isolated and identified as S. aureus, S hyicus, S. epidermidis, S. intermedius, S. cohnii, S. sciuri, S. schleirferi and S. delphini. Strains showing identical biochemical profile, from the same sample, were grouped into a pool and them were induced to produce SE and TSST-1. The detection of toxins was made by the OSP (Optimum Sensivity Plate) method and the cellophane-over-agar technique. It was identified SEA, SEB, SEC, SED and TSST-1 in different percentages. From the 138 formed pools, 91 produced, at least, one or more toxin, including TSST-1. From the enterotoxigenic pools, 24.6% were coagulase positive, while 41.3% were negative. The presence of entorotoxigenic negative coagulase Staphylococcus strains isolated from milk samples is important in relation to public health.
raw milk; Staphylococcus; enterotoxins; TSST-1