Abstract
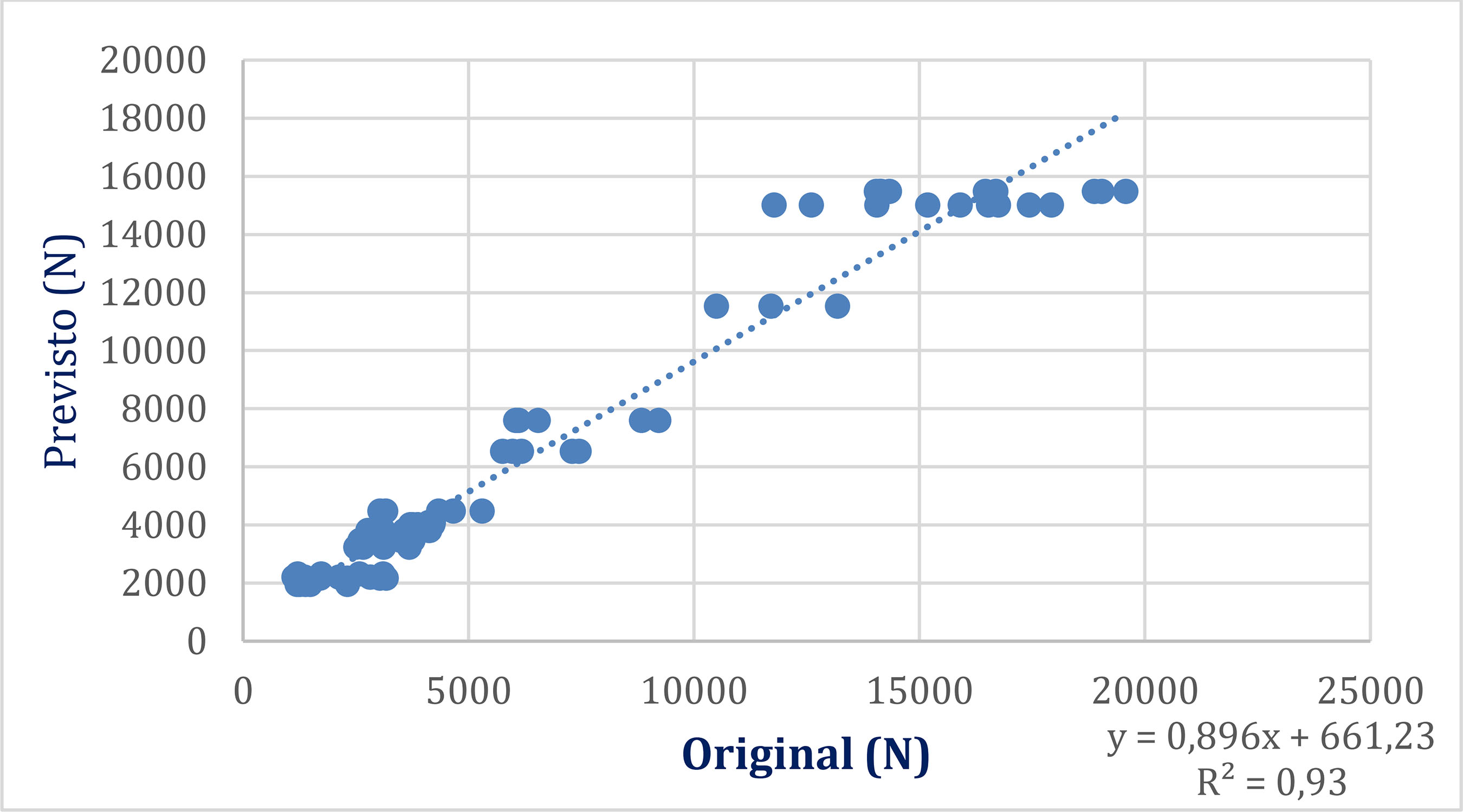
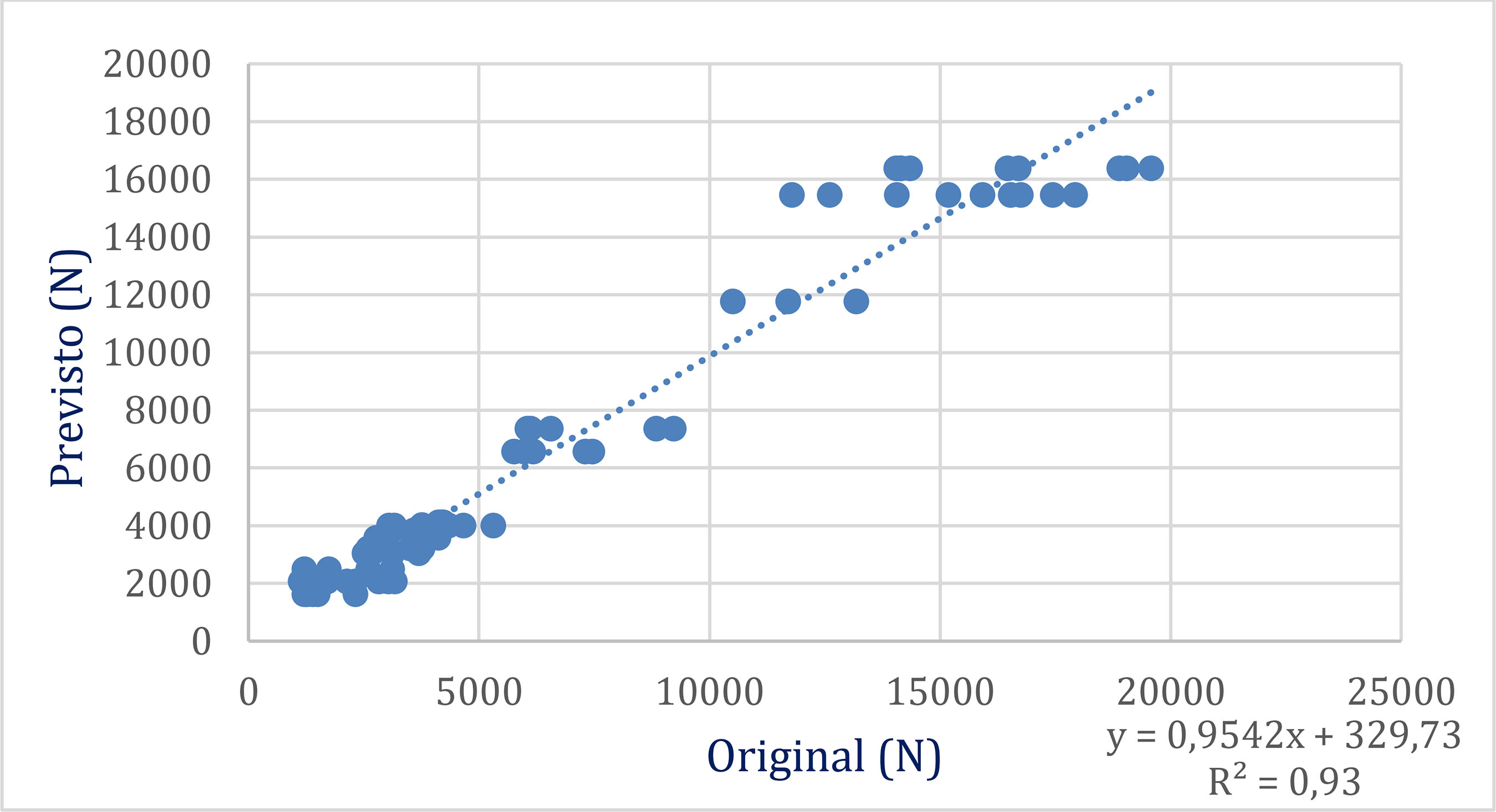
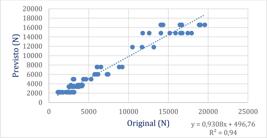
This study aims to develop a predictive model using reinforcement learning algorithms. The main objective is to propose an alternative method for predicting the bond strength between steel and concrete. The results obtained indicate that the intelligent systems developed are effective in estimating the maximum bond strength, with performance comparable to that of other studies on the same topic. It was observed that there is a correlation between a test parameter—the coefficient of variation—and the performance of the computational method, reducing computational error. The use of the “Indicator” metric enabled comparison with other studies in the literature. It was observed that the Indicator and R² are inversely proportional, and it was also noted that there is a correlation between these two metrics in all the studies analyzed. Finally, it is concluded that reinforcement algorithms are promising tools for dealing with complex problems characterized by high non-linearity and multiple variables, such as steel-concrete adhesion, since the results point to the viability of these intelligent systems as an alternative and reliable method for predicting maximum adhesion strength.
Keywords
Intelligent systems; Bond strength; Boosting algoritms

 Reinforcement algorithms in predicting the maximum steel-concrete bond strength in thin bars
Reinforcement algorithms in predicting the maximum steel-concrete bond strength in thin bars Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
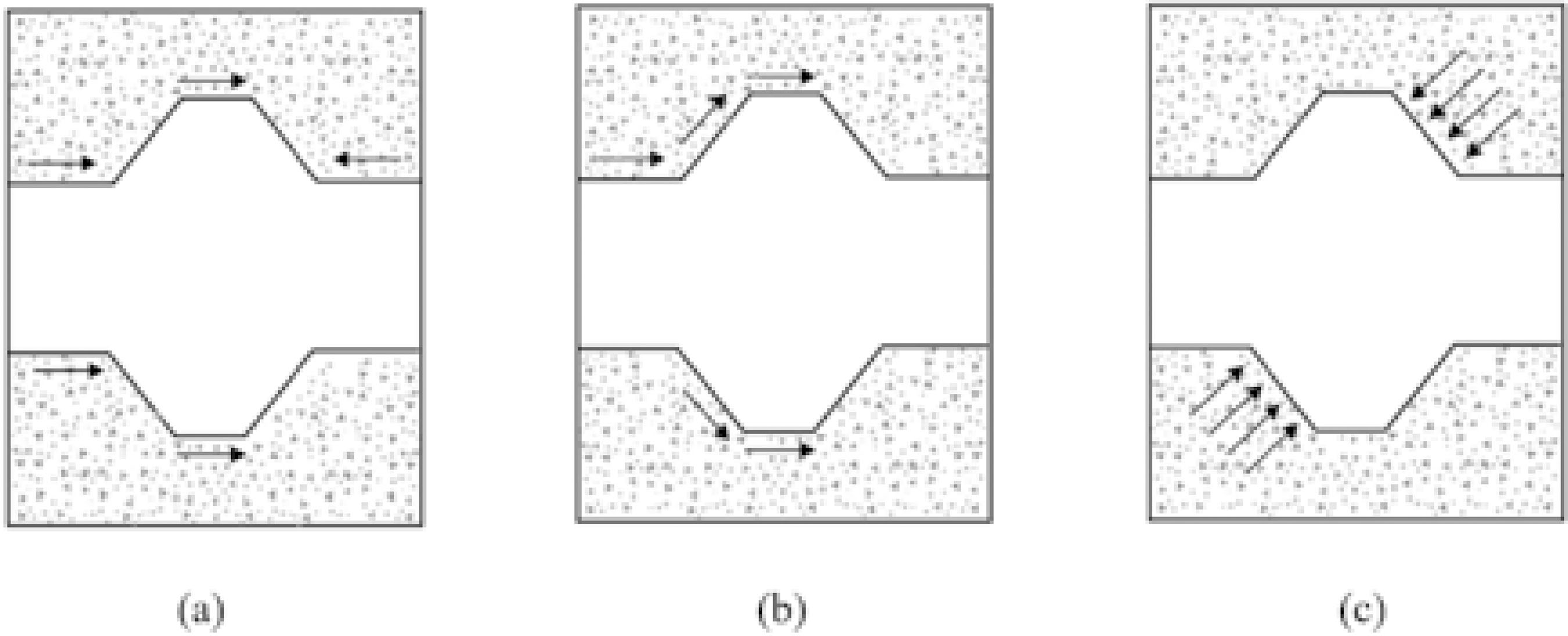 Fonte:
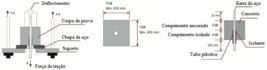
Fonte:  Fonte: adaptado de
Fonte: adaptado de  Fonte:
Fonte:  Fonte: Fusco (1995).
Fonte: Fusco (1995).
 Fonte: adaptado de
Fonte: adaptado de