Abstract
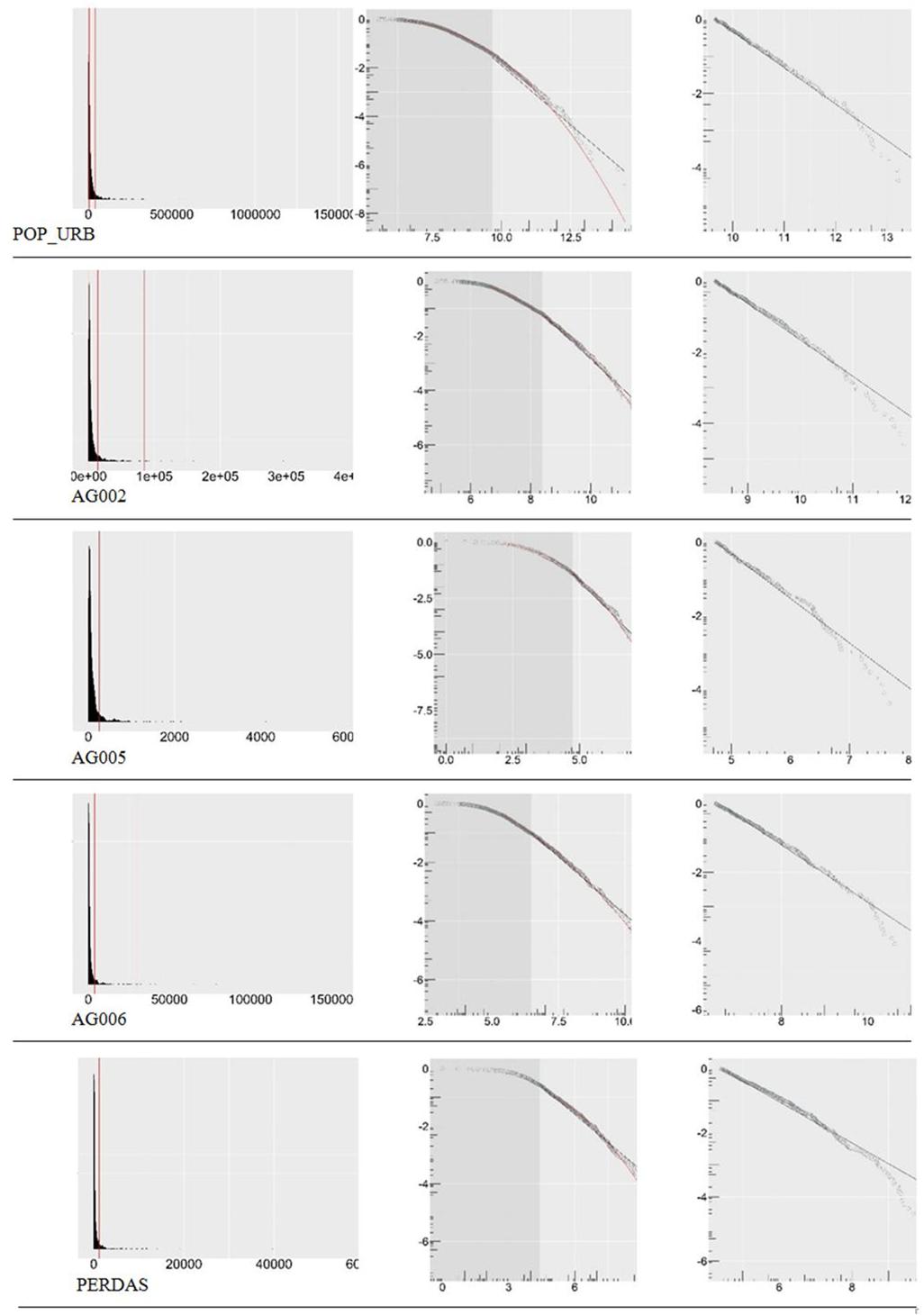
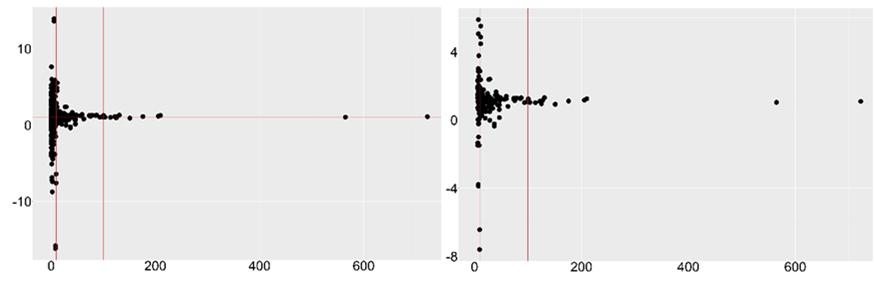
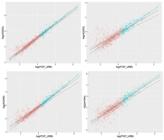
The drinking water supply to urban populations suffers losses caused by leaks, theft and unauthorised use. This by-product of urbanisation is disproportionately greater in large cities, suggesting that it derives from complex socio-technical mechanisms, with apparently unpredictable behaviours as populations and social activities increase. With the purpose of verifying this hypothesis and seek for quantitative regularities between city size, the size of the utilities and the amount of losses, we analysed a network of municipalities in southern Brazil from the perspective of the "New Science of Cities”, using simple statistical techniques. We found highly hierarchical distributions, typical of natural complex systems, as well as non-linear scaling regimes between the cities’ population and the selected indicators: exponent <1 for the water distribution system variables (network extension, households connected, and volume produced) and > 1 for the volume of losses. Water losses, consistently presented higher per capita volumes as the population increased, with “increasing returns” comparable to products of social activity such as university degrees or bank deposits. The study presents a complementary approach to the problem, suggesting a certain degree of predictability of the losses at a regional level that can inform policy-making and support better decisions regarding the supply of drinking water in Brazilian cities.
Keywords:
Complexity; Complex socio-technical systems; Water distribution systems; Water losses; Urban scaling laws

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
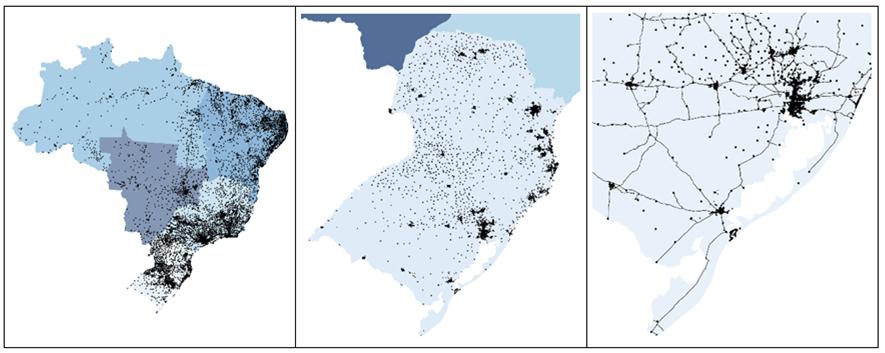 Fonte: adaptado de dados espaciais de
Fonte: adaptado de dados espaciais de