Abstract
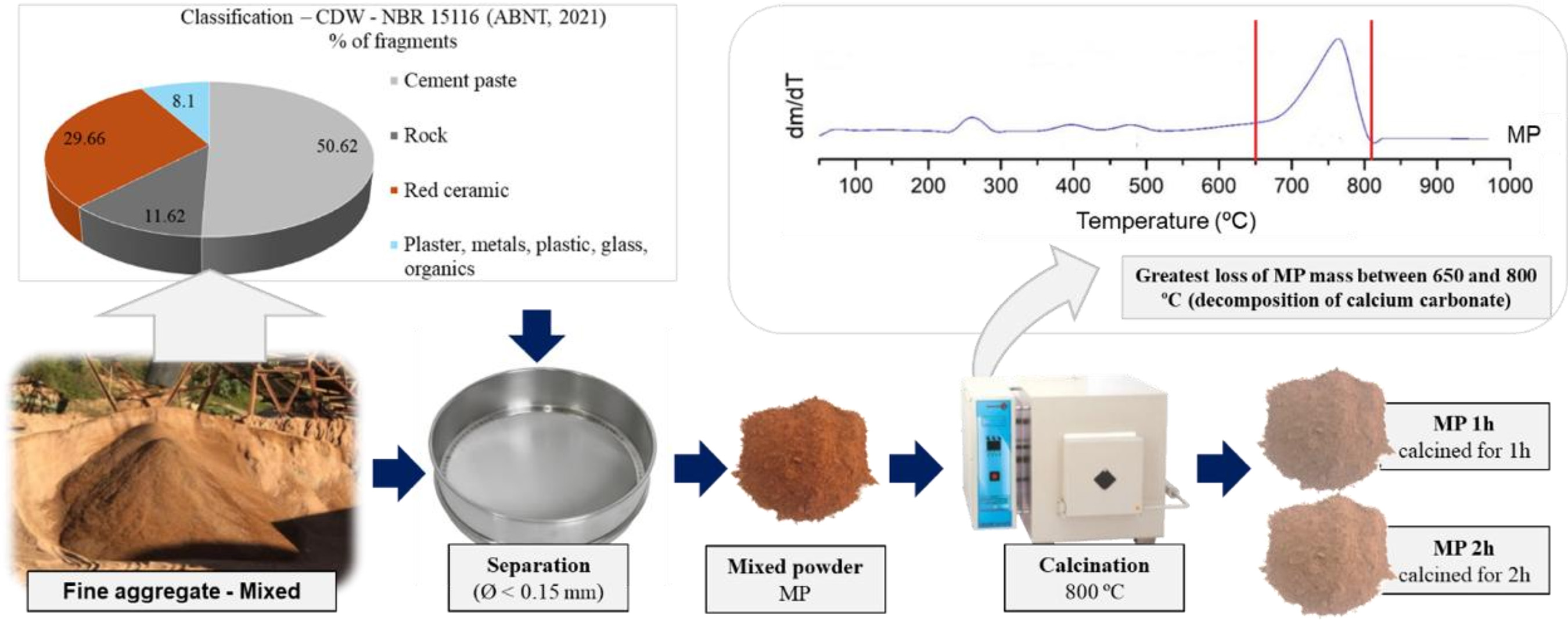
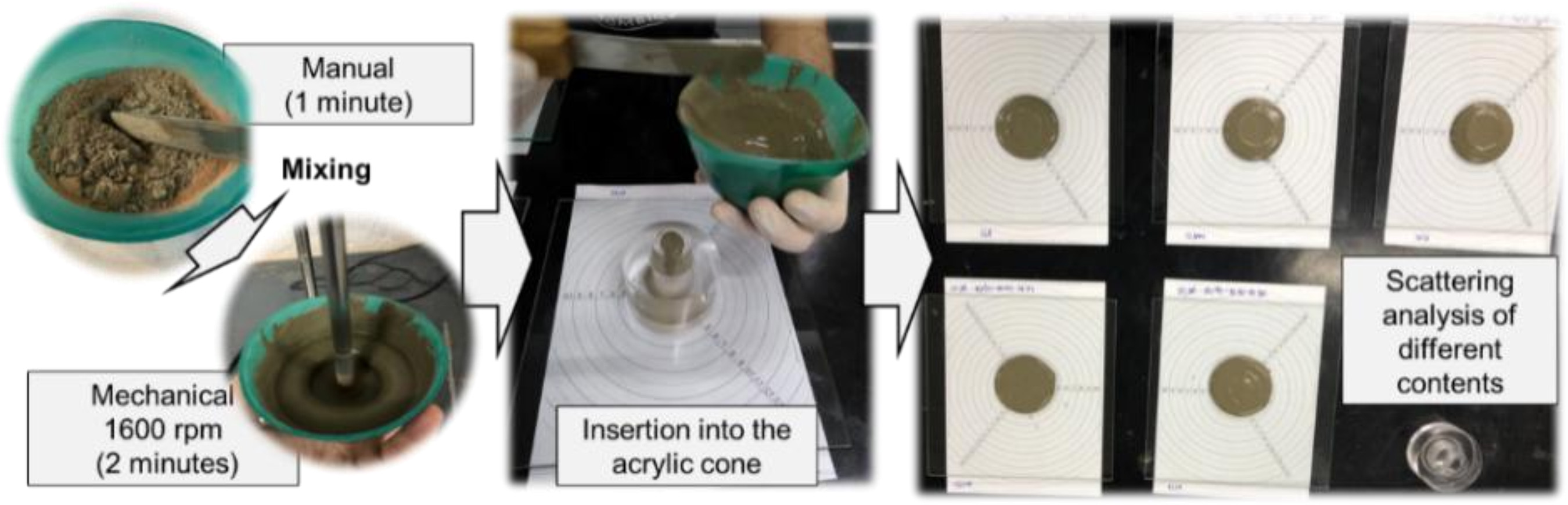
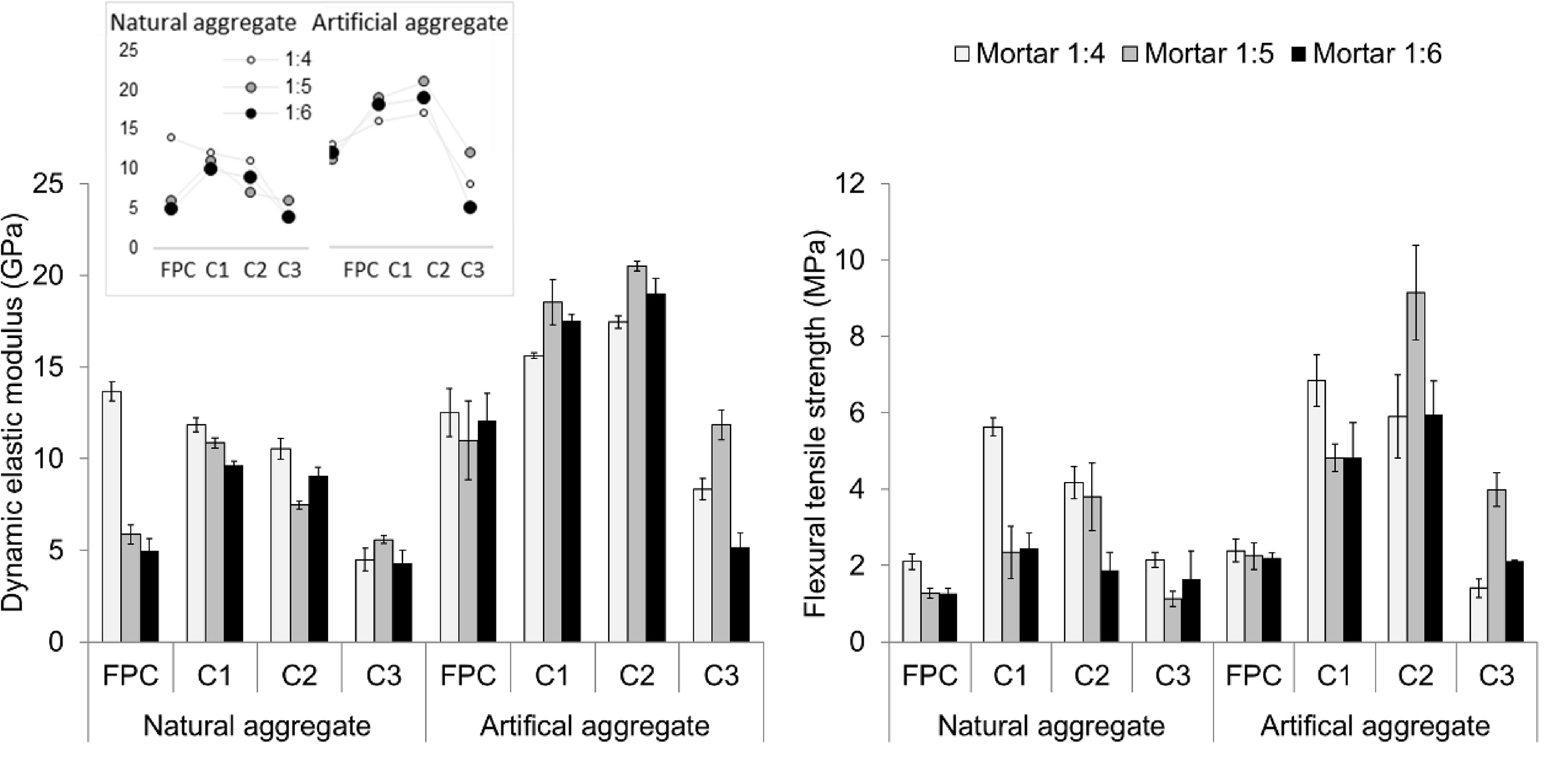
The circularity in industrial processes is fundamental to different waste type applications. On this context, this study uses mixed construction and demolition waste (CDW) powders, calcined at 800 ºC, to replace Portland cement at 25 to 45% levels in coating mortars with natural and artificial fine aggregates (crushed sand). Mortars were produced with 1:4, 1:5, and 1:6 ratios (cement: fine aggregate), assessing fresh-state properties and hardened-state properties. Environmental performance was evaluated considering CO2 emissions and binder consumption. Mortars containing 25% recycled powders showed similar mechanical performance to mortars with reference Portland cement (FPC). Mixtures with artificial aggregates incorporated less air, reducing porosity and water absorption, improving mechanical performance by up to five times compared to natural aggregates. The CDW powder use reduced mortars carbon emissions up to 30%, while the artificial aggregates presence reduced emissions up to 6%. So, this study demonstrates the mixed CDW powders potential as a replacement for cement and the artificial aggregate potential to improve aspects related to circular economy and CO2 emissions reduction.
Keywords
Coating Mortars; Circular economy; Low carbon technologies; SCM

 Performance of mortars with calcined construction waste powder and natural or artificial aggregates
Performance of mortars with calcined construction waste powder and natural or artificial aggregates Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
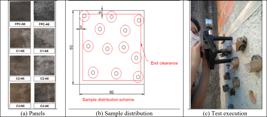 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
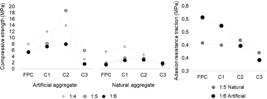 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
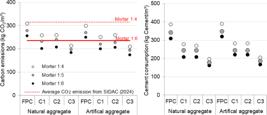 Thumbnail
Thumbnail