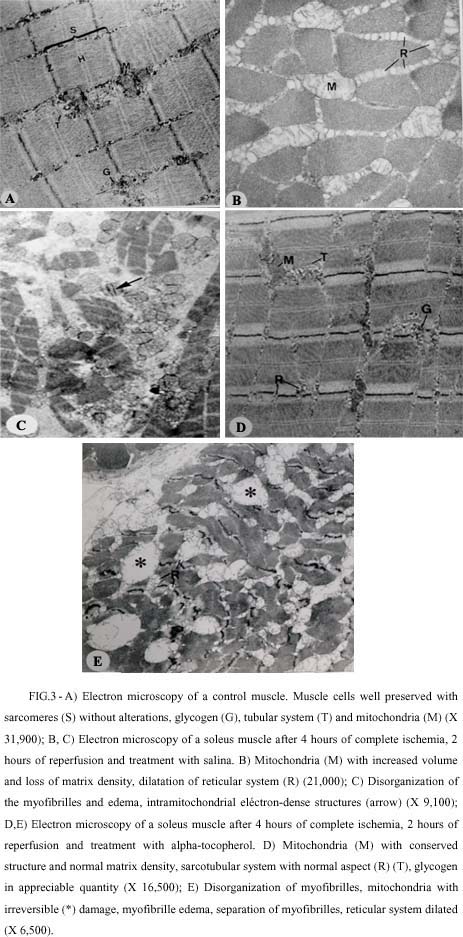
Studies indicate that oxygen-derived free radicals may play a major role in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Alpha-tocopherol acts in vivo as a free radical scavenger. Our purpose was to elucidate whether alpha-tocopherol could change the evolution of ischemia/reperfusion in the right hindlimb of rats. The animals were randomly allocated in the following groups: Group 1(G1)- control without ischemia. Groups 2 and 3(G2,3): four hours ischemia and two hours reperfusion. The animals of group 2 were treated with saline and those of the group 3, treated with alpha-tocopherol, 50 mg/Kg. Parameters were the foot volume and circumference, 99mTc-Pyrophosfate uptake in the soleus muscle, plasmatic creatine-phosphokinase (CPK), and transmition eletronic microscopy (TEM)of muscle cells. The foot volume and circumference of the animals of G2 were significantly greater than in G1. In the G3 these measurements did not differ from the G1. Pyrophosphate uptake and CPK measurements were increased in G2,G3 when compared to the animals of G1, but there were no differences between the ischemic groups. Cell injury, when examined by TEM, was less severe in two of three animals of G3, when compared to the G2. Conclusion: The treatment with alpha-tocopherol diminuished edema formation, but only partially protected muscle cells from injury.
Alpha-tocopherol; Ischemia; Reperfusion; Rats