PURPOSE:
To study the possible potentiation of the carcinogenic effects of ultraviolet radiation associated with an organophosphate pesticide.
METHODS:
Forty Wistar rats were assigned into four groups (n=10 each) randomized according to the procedures: group A received only UVR-B radiation; group B, UVR-B for eight weeks followed by a seven week period of pesticide exposure; group C, UVR-B + pesticide concomitantly: group D, only pesticide application. At the end of the fifth, tenth and fifteenth weeks the animals were photographed. Skin biopsy and histopathological study with Hematoxylin-Eosin were done on the fifteenth week. Statistical analysis with Fisher's and Sign (unilateral) tests, 5% value for significance.
RESULTS:
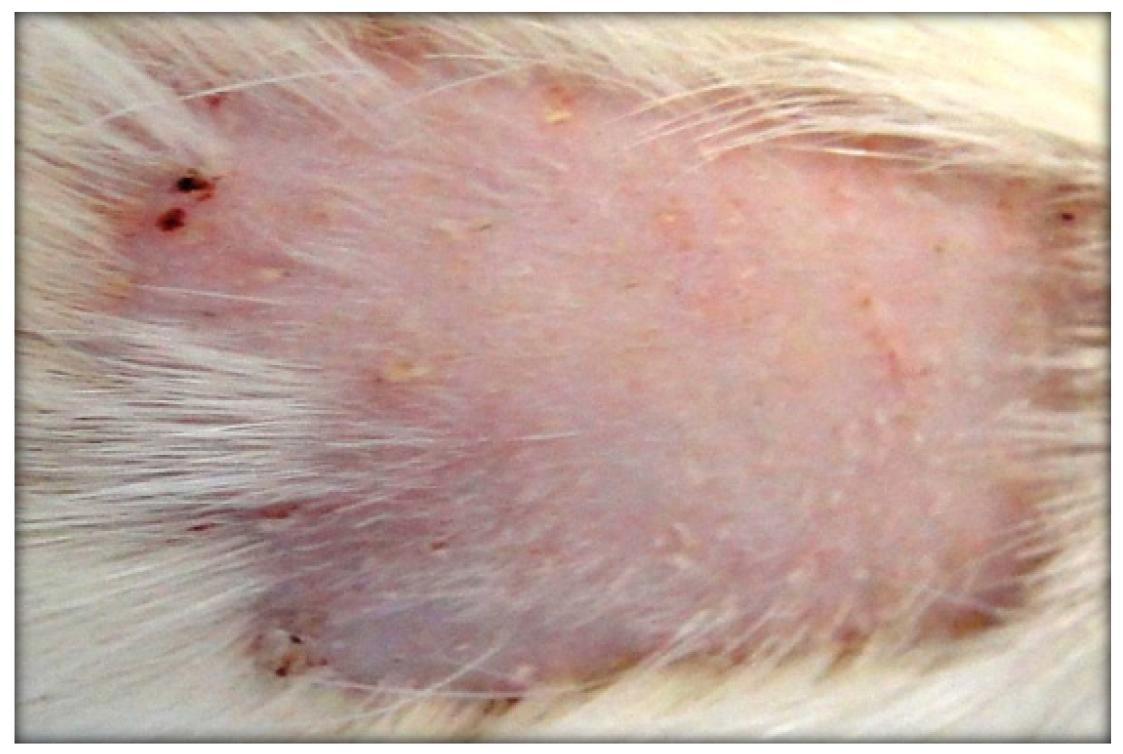
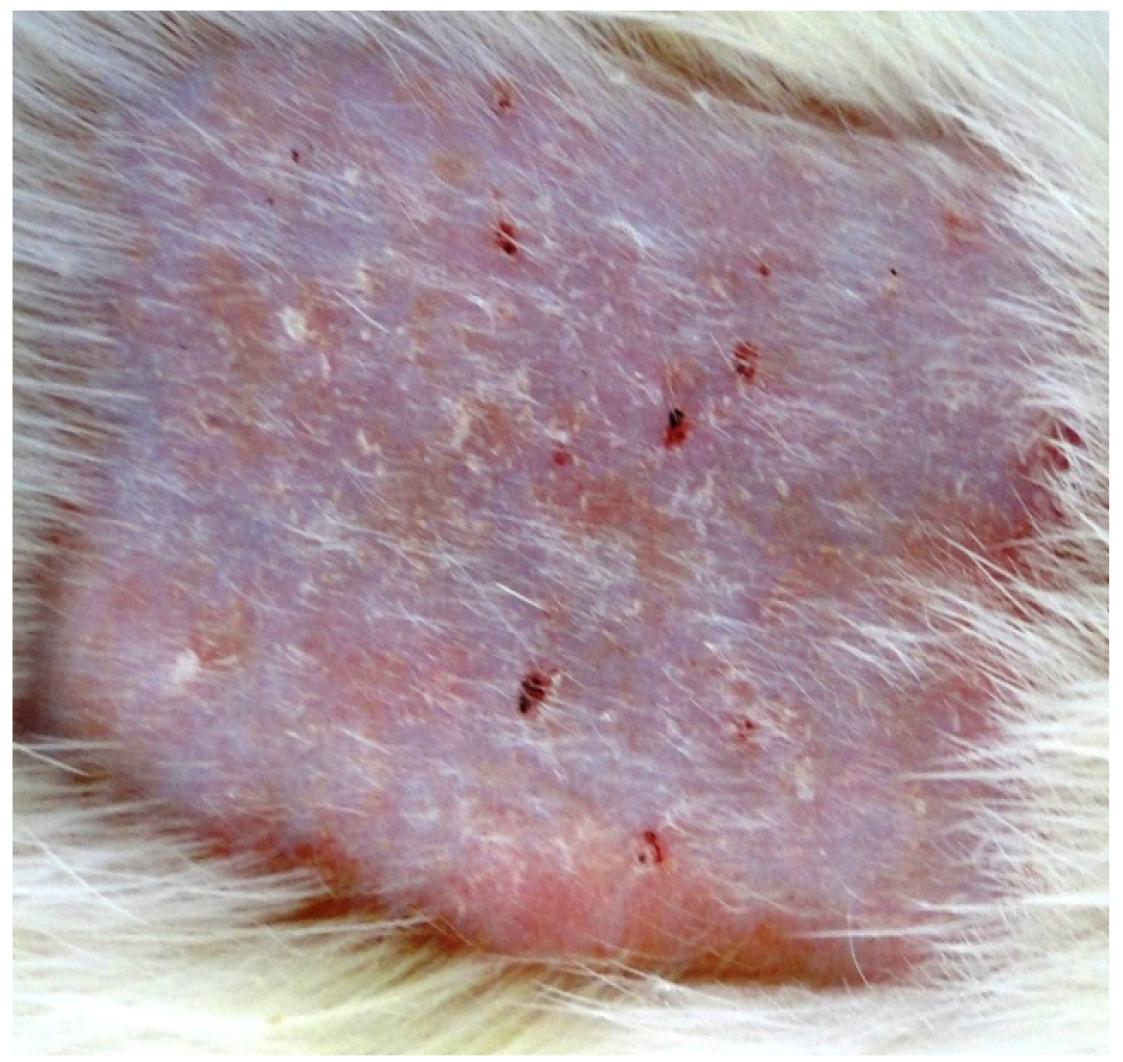
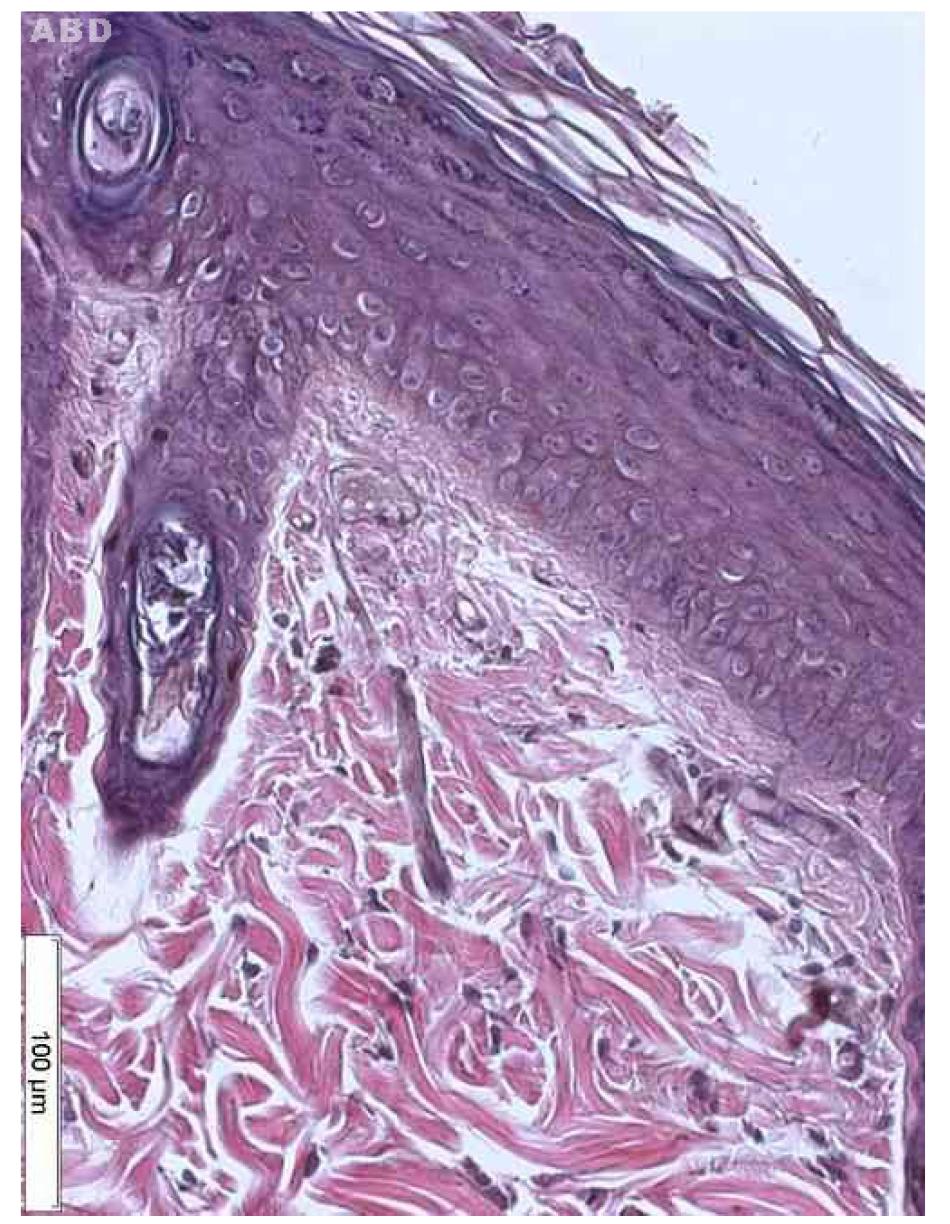
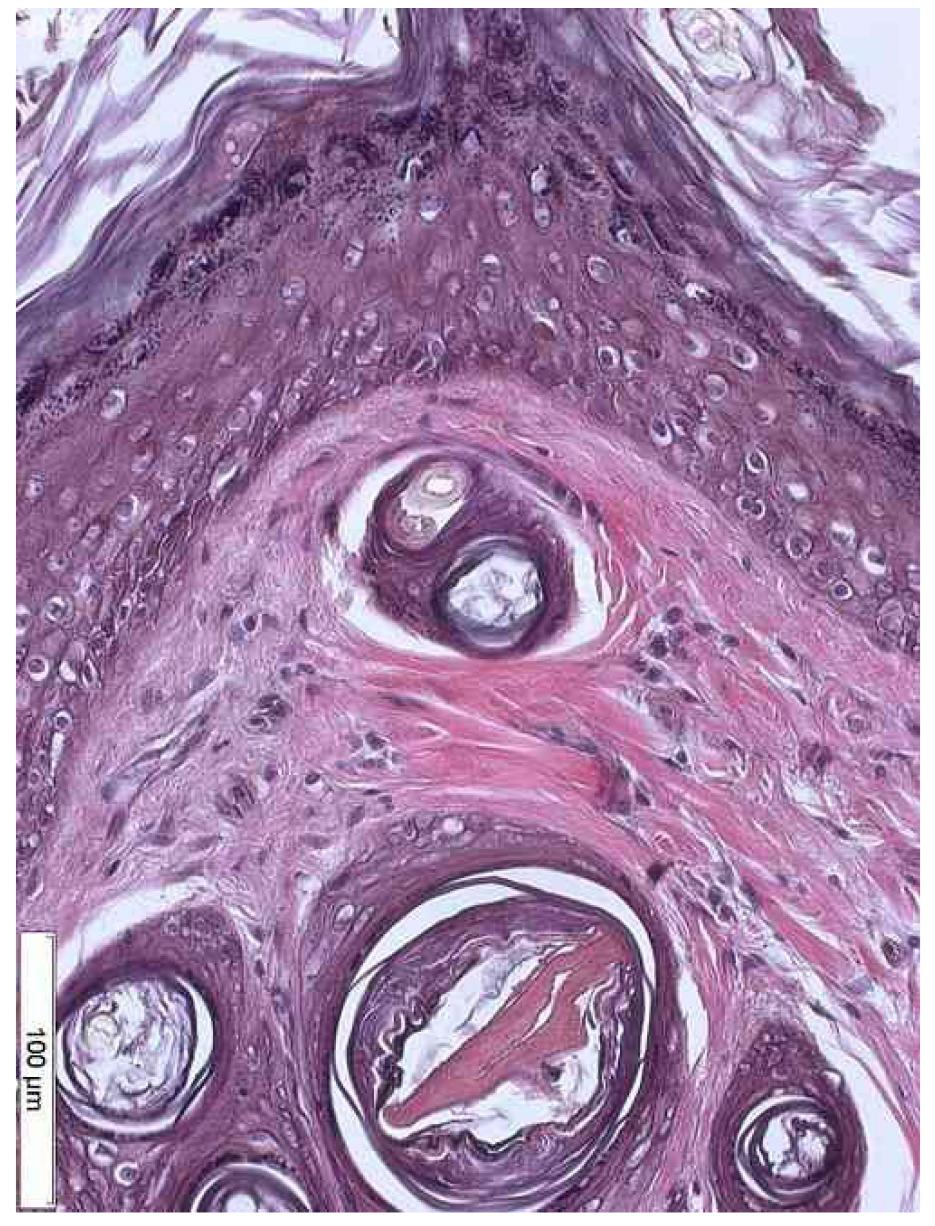
Macroscopic lesions in the group A evolved from the erythema to erythema + desquamation. The groups B and C, with the association of two carcinogens, and group D presented evolution to keratosis, with higher incidence in group D. The histology showed a significant increase in the severity of injuries when the UVR-B and the pesticide were applied simultaneously, leading to cellular atypia.
CONCLUSIONS:
Concurrent association of UVR-B to organophosphate pesticide produced more severe lesions microscopically, although this has not been so apparent macroscopically. In daily practice the clinical evaluation should be complemented with laboratory evaluation.
Epidermis; Solar Radiation; Skin Neoplasms; Organophosphates; Rats