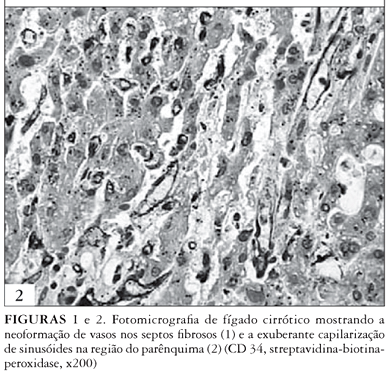
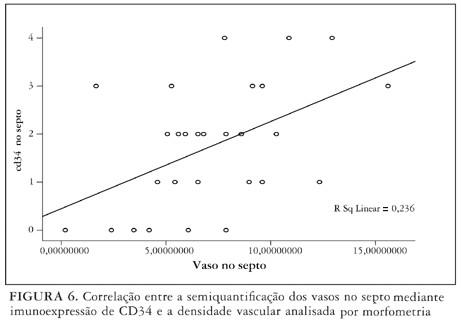
BAKGROUND: Fibrosis has been the most cited variable in cirrhosis, but major alterations in hepatic vascularization have been pointed as basic elements in the physiopathology of the illness and its complications as portal hypertension, hepatic failure and hepatocellular carcinoma. METHODS: The present study aims at assessing microvascular density in 35 cases of necropsies of cirrhotic patients by immunohistochemical detection of endothelial marker CD34, comparing semi-quantification with morphometric quantitative method, also searching for a possible relation of vascular alterations with the main causal agents, injury patterns and major clinical complications. RESULTS: A significant association was detected between semi-quantitative and quantitative approach of microvessel density in parenchyma, but not in septa. No significant association was detected between neovascularization and any specific clinical complication of cirrhosis. Under our standpoint, the main achievement of the present study was the demonstration that the vascular neoformation in hepatic parenchyma is significantly higher in cirrhosis associated with chronic hepatitis than in cirrhosis resulting from steatohepatitis. CONCLUSION: These findings require further clinical studies to assess the hypothesis that the rearrangement of liver microcirculation through the detection of CD34 might be relevant in prognostic assessment of cirrhotic patients.
Liver cirrhosis; Hepatitis, chronic; Fatty liver; Antigens, CD34