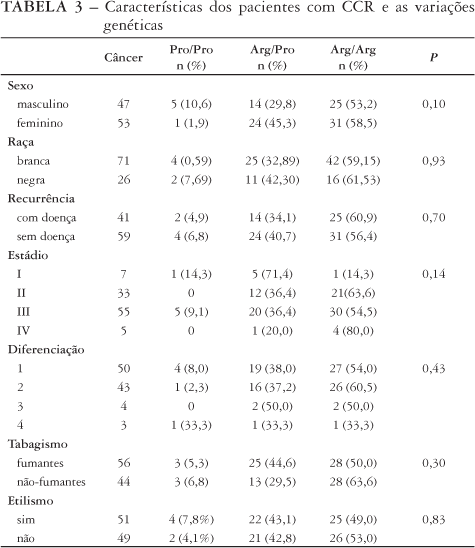
BACKGROUND: Polymorphisms are genetic variations that can occur in sequences of codons, leading to defective proteins. p53 is the most commonly gene affected in human cancer. The polymorphism of this gene occurs by a substitution of a base in codon 72 and may increase the risk of cancer. AIM: To investigate the possible association between p53 arginine/72 proline polymorphism and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. PATIENTS AND METHODS: This polymorphism was studied by polymerization chain reaction using specific primers in 100 patients with colorectal cancer paired by sex and age to 100 patients without cancer. Alcohol and tobacco used by all the patients and clinical aspects as stage, grade of differentiation and recurrence in the case group was compared with the genotype analyzed. RESULTS: The frequency of homozygosis for arginine was 56% in the cancer group and 58% in the control group. No significant difference was observed among both groups. This genotype was more frequent in colorectal cancer patients stage IV than in stage I (80% versus 14%). There was no significant difference between genotypes and alcohol, tobacco, grade of differentiation or recurrence. CONCLUSION: Homozygosity for arginine was the most prevalent genotype in both groups. The frequency of codon 72 proline/arginine p53 gene polymorphism was not correlated with a higher risk of colorectal cancer. Arginine/arginine genotype was more prevalent in advanced cancer patients (stage IV).
Polymorphism (genetics); Genes, p53; Colorectal neoplasms; Prognosis