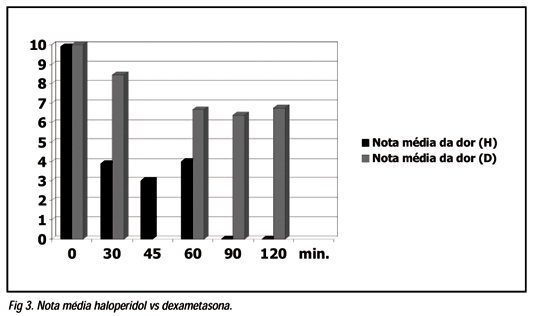
We studied the efficacy of dexametasone (4 mg) and haloperidol (5 mg) in the treatment of migraine in the emergency room. Twenty nine patients who had diagnosis of migraine according to the International Headache Society criteria and were evaluated for a painful episode at the emergency room of Santa Casa of São Paulo were included. All the patients scored their pain in 10 when evaluated, even after the use of intravenous analgesia (dipyrone). Fourteen patients were treated with haloperidol and the remaining 15 received dexametasone. The patients were asked about pain intensity at 30, 60, 90 and 120 minutes after the use of either the drugs. Both drugs were equally efficient in pain relief after two hours. Patients who were treated with haloperidol showed an important improvement (more than 50% of improve in the analogic pain scale) in the first 30 minutes. The dexametasone treated patients only reached this grade of analgesia after 120 minutes. Although we studied a small serie of patients, our data suggest that both drugs are efficient in the treatment of a refractory migraine attack. Haloperidol seemed to work quickly in pain relief. No important side effects were observed in neither groups.
migraine; haloperidol; dexametasone; emergency room; side effects