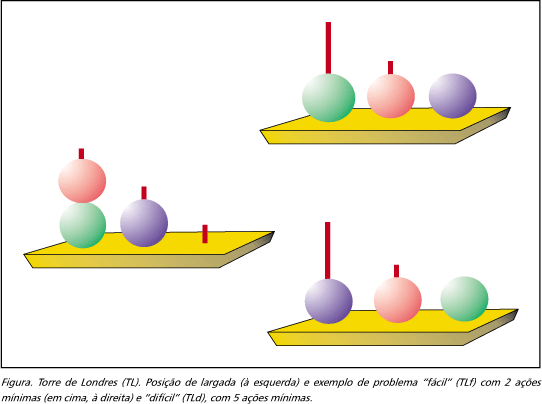
The concept of "executive behavior" encompasses a set of abilities which are critical for the organization of thought and behavior. To test the hypothesis that executive behavior is composed of multiple modules we investigated the performance of 61 normal adults on two widely used executive tasks, the Wisconsin Card Sorting (WCST) and the Tower of London (TOL) tests. We hypothesized that if executive behavior were composed of multiple modules, the main dimensions of each task would be weakly, if at all, statistically related. We also tested the hypothesis that occupational functioning would be related to executive performance. Our results revealed no significant association between the WCST and TOL tasks, favoring the idea that executive behavior is made up of multiple neuropsychological dimensions. Secondly, men fared significantly better than women on the difficult (4 and 5-moves) TOL puzzles. Finally, there was a significant association between performance on the difficult TOL puzzles and level of occupational functioning. These findings may explain certain dissociations in executive behavior commonly observed in patients with focal or diffuse brain damage. If replicated, they might be useful in the prediction of success in cognitive rehabilitation programs.
executive behavior; frontal lobes; Tower of London; Wisconsin Card Sorting Test