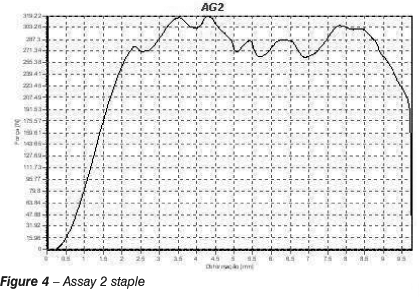
INTRODUCTION: Tarsometatarsal arthrodeses are an effective therapeutic alternative for treating symptomatic osteoarthroses of the Lisfranc joint. Stabilization methods available include: Kirschner's wires, cortical screws, plates and screws and staples. The stability provided and the surgical technique employed with each material is discussed in literature. PURPOSE: To compare compression forces and biomechanical stability of tarsometatarsal joint fixation with cortical screws and staples. CASE SERIES AND METHOD: Ten fresh male cadavers with ages ranging from 35 to 49 years were selected and submitted to bilateral dissection of the cuboidal and 4th metatarsal bones, with joint surfaces decortification and fixation with cortical screw - Cortical Screw 3.5mm Impol, and Uni-clip® Staple 2.0 NewDeal. RESULTS: All the 20 biomechanical assays were completed. The statistical analysis of the methods using staples vs. cortical screw concerning accrued energy until reaching the assay's peak force p= 0.047, and the accrued energy until the completion of the assay p= 0.047 showed a significant difference. CONCLUSION: Load peaks supported by staples and cortical screws are significantly reduced with age. Superior force values are found for staples in osteoporotic bones. The accrued energy on graphs' work areas in assays with staples is shown to be statistically superior to cortical screws' values.
Foot joints; Arthrodesis; Internal fixators; Biomechanics