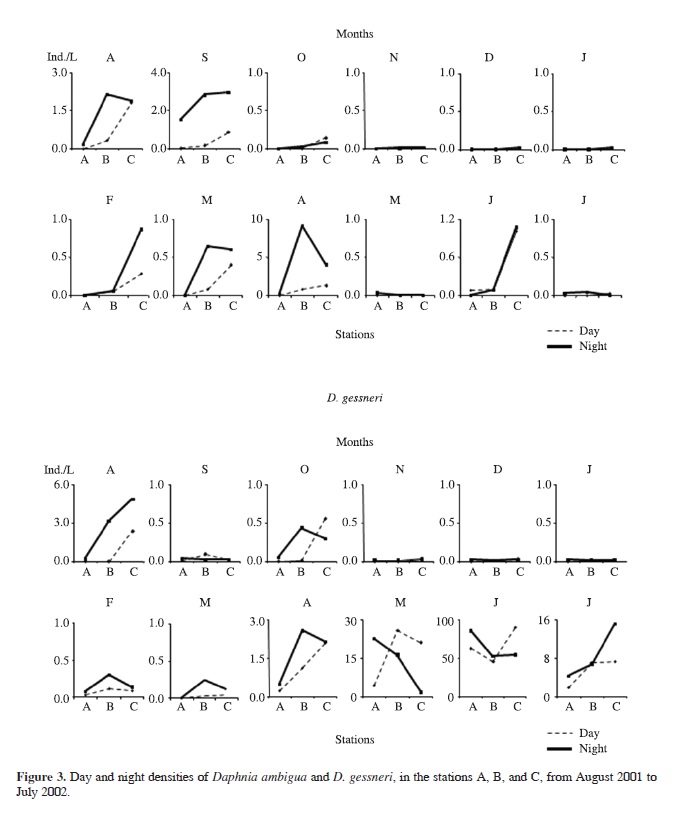
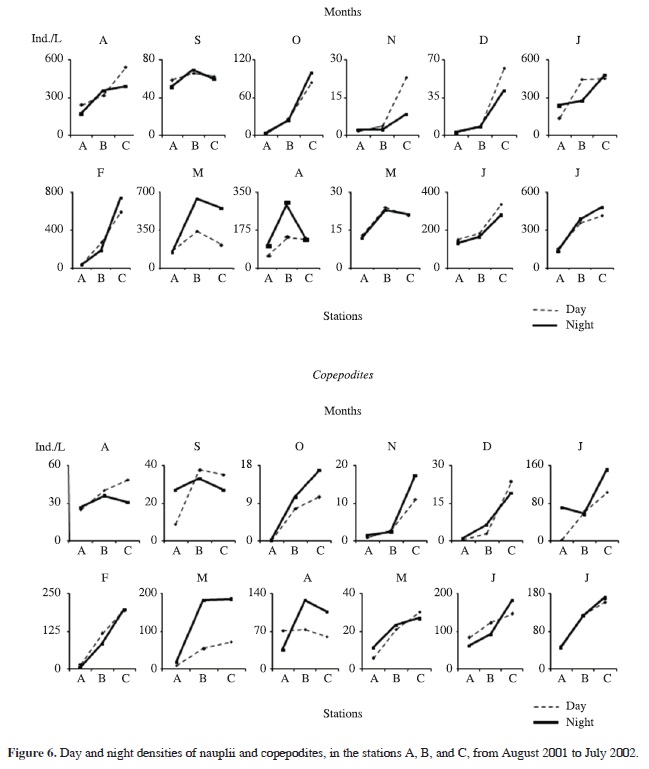
The focus of this study is to investigate if microcrustaceans undergo diel horizontal migration (DHM) in a tropical shallow lake on a yearly basis and analyse the adaptive value regarding predation. Abundance of invertebrate predators, chaoborid larvae and water mites, and microcrustaceans (cladocerans and copepods) were evaluated on a monthly basis in three stations located on a transect during the day and at night. Both invertebrate predators were predominantly pelagic. Cladocerans did not undergo significant DHM, distributing indistinctly onshore and offshore or being mostly pelagic. Nauplii, copepodites of two copepod species and adults of Tropocyclops prasinus meridionalis Kiefer were mostly distributed offshore, and did not perform DHM. The limnological features (temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, and conductivity) were suitable for the organisms in both zones of the lake. Algal food concentration was a little lower in the littoral than in the limnetic zone during the day, but it seems to be suitable for the organisms. However, as the algae quality was not evaluated, it is not possible to be conclusive concerning its influence. The results indicated that DHM was not performed by the microcrustaceans and is not, therefore, a strategy for decreasing predation by both invertebrates, Chaoborus brasiliensis Theobald and Krendowskia sp., on a yearly basis in this shallow lake.
Chaoborus; water mites; cladocerans; copepods; food; DHM