ABSTRACT
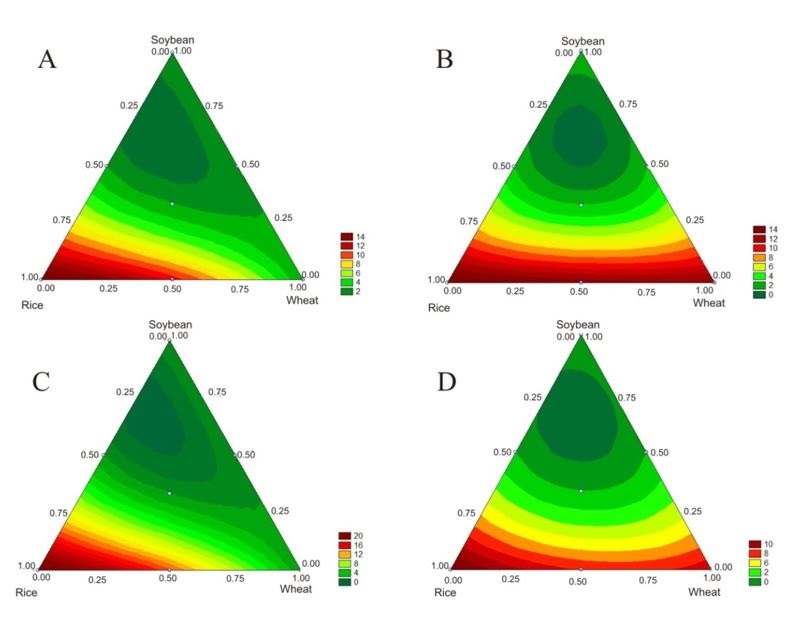
Filamentous fungi can easily degrade agro-industrial wastes in solid-state fermentation processes, synthesizing many important commercial biocompounds, such as lipolytic enzymes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of the composition of the solid culture medium on the production of lipolytic enzymes by the fungus Aspergillus niger. Rice, wheat and soybean bran were mixed to prepare the culture medium, which was supplemented with glucose, glycerol or soybean oil. Four mixture experimental designs were used to find the best medium for enzyme production. According to our results, the highest lipolytic activity values were achieved with a mixture of rice bran and glycerol (19.844 U·g-1) or with rice bran only (13.267 U·g-1). Thus, the lipolytic enzyme could be produced without any additional carbon source apart from rice bran, although glycerol addition induced a higher production.
KEYWORDS
Enzyme; Fungus; Agro-industrial wastes; Carbon source.

 Thumbnail
Thumbnail
 Thumbnail
Thumbnail