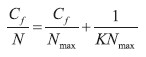Nickel biosorption ability was evaluated in two bacterial strains: Acinetobacter baumannii UCR-2971 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa UCR-2957, resulting in greatest adsorption at pH 4.5 and a residence time of 100 minutes. Biosorption isotherms showed that the process follows the Langmuir model. The maximum adsorption rates (Nmax) were 8.8 and 5.7 mg·g-1 for A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa, respectively; however, affinity constants suggest that P. aeruginosa (K=1.28) has higher affinity for nickel than A. baumannii (K=0.68). It is suggested that both strains could be used for wastewater treatment, as long as the concentration of Ni2+ is within the range of mg·L-1.
biosorption; nickel; Acinetobacter baumannii; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; wastewater treatment