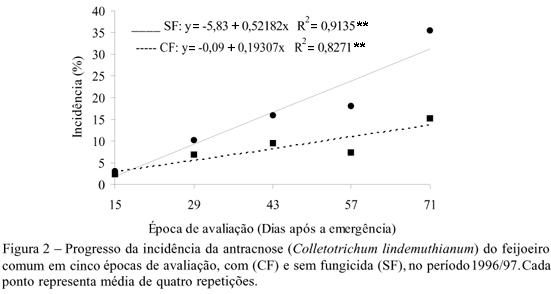
In Minas Gerais the anthracnose is one of the most important leaf diseases of the common bean due to occur at various planting time and to reduce the production. The present experiment was performed aiming to evaluate occurrence, progress of the disease and the efficiency of fungicide on the control of bean anthracnose. Plots with and without fungicide treatment (Thiophanate methyl + Chlorothalonil, 240 + 600g a. i./ha) were evaluated in five times of evaluation during 24 sowing times of bean cultivar Carioca, between April/96 and March/97. The occurrence of the anthracnose was not verified during february and march of 1997. Treatment with fungicide resulted in the lower disease severity and higher yield, mainly in the months of higher severity of the disease. There was significant correlation between the severity and the maximum and minimum temperature and relative humidity 43, 57 and 71 days after emergency. There was a negative correlation between severity of the disease and yelds.
Phaseolus vulgaris L.; Colletotrichum lindemuthianum; Epidemiology