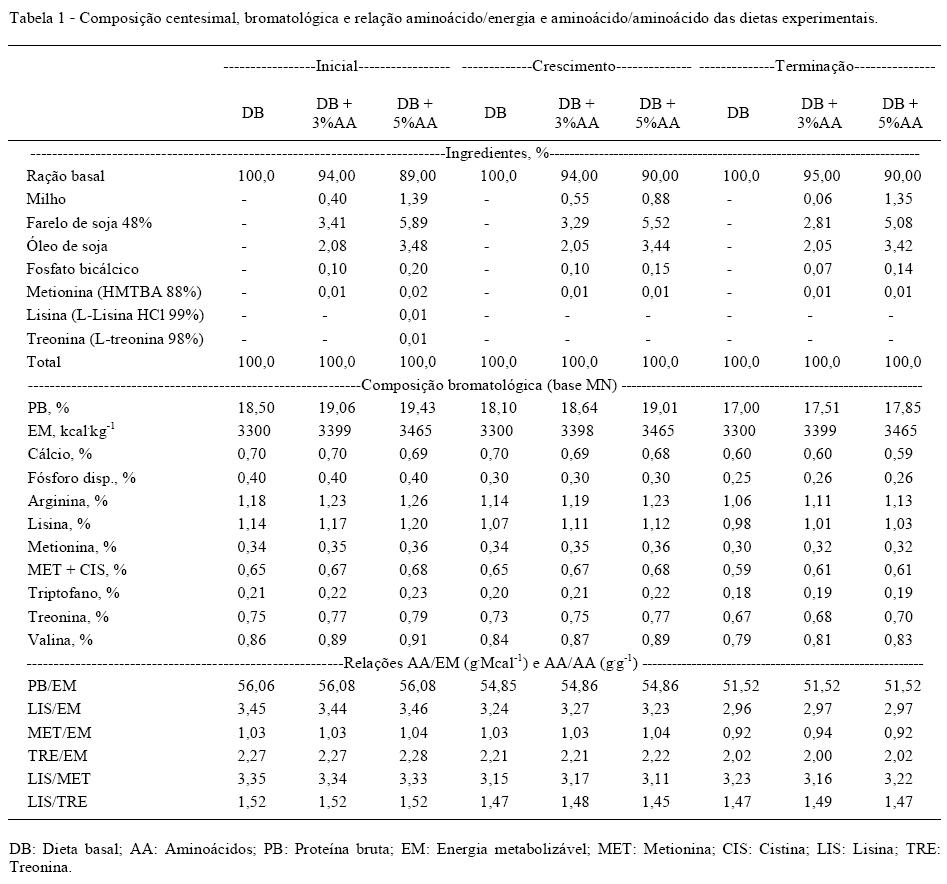
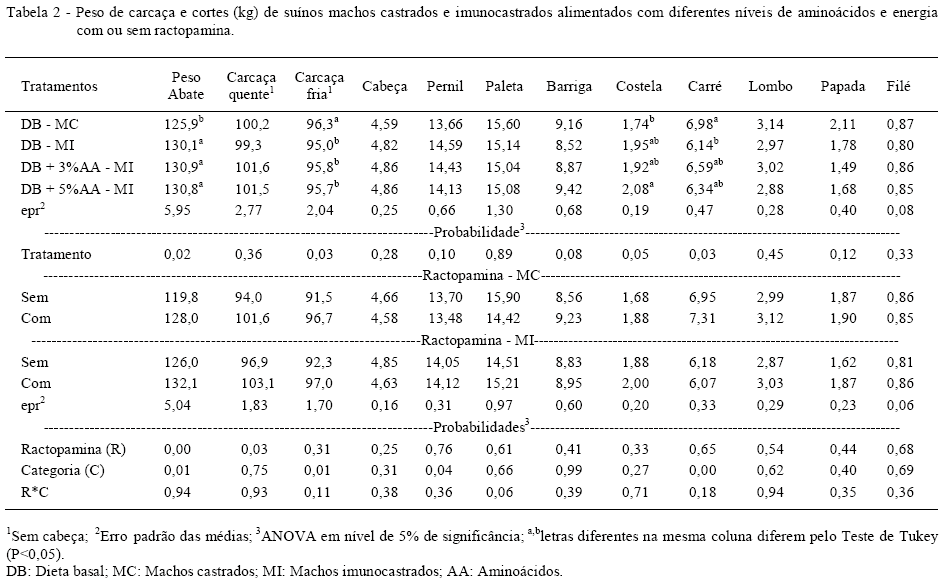
The study was carried out to evaluate the carcass characteristics and meat of surgically castrated and immunocastrated pigs fed with different nutritional levels. The animals were distribuited in a completely randomized experimental design with four main treatments (T1-surgically castrated pigs fed with basal diet; T2-immunocastrated pigs fed with basal diet; T3-immunocastrated pigs fed with basal diet+3% amino acids and energy; T4-immunocastrated pigs fed with basal diet+5% amino acids and energy) and two secondary treatments with or without ractopamine within each main treatment. The surgically castrated pigs had slaughter weight 3.3% lower (P<0.05), cold carcass weight 1.4% higher (P<0.05) and loin chop weight 13% higher (P<0.05) compared to immunocastred pigs. The immunocastrated pigs supplemented with 5% more amino acids and energy had rib 19% more heavier (P<0.05) and higher values (P<0.05) in the color b* (yellow-blue) in the meat to 45min and 24h post-slaughter compared with surgically castrated pigs fed with basal diet. Supplementation with 5% amino acids and energy increases weight and yield of rib and changes the value of color b* (yellow-blue) in the meat to 45min and 24h post-slaughter male pigs immunocastrated.
energy; post-slaughter; protein; ractopamine; swine production

 Carcass characteristics and meat of surgically castrated and immunocastrated pigs fed different nutritional levels
Carcass characteristics and meat of surgically castrated and immunocastrated pigs fed different nutritional levels