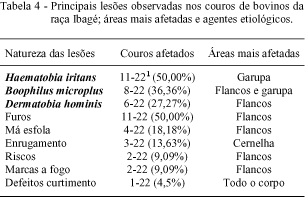
Twenty two male 2- year- old Ibagé bovines at the beginning of the experiment were selected. They were divided into two groups of 11 bovines each. One group was treated with insecticide at 14 days intervals and the other remained as control. After that the animals were slaughtered and the respective leather sent to the tannery where they were tanned and evaluated in two stages, the Wet-Blue (leather treated in chromium, still humid and bluish) and the total tanning. Animals weight, carcasses weight and dressing percentage were recorded and there was no correlation between infestation by the horn fly and those parameters. At slaughter, samples of the flank areas and the back of the animals were collected and processed for histology studies, which revealed the presence of a perivascular inflammatory infiltration with eosinophils and few mononuclear cells (lymphocytes and plasma cells) at the superficial dermis in which 16 out of 19 samples (84.21%) were mild in 2 out of 19 samples (10.52%) were moderate and in 1 out of 19 samples (5. 26%) was marked. In the tanning phase called as Wet-blue, the classification of the leathers was as follows: 8 out 22 (36.36%) type "A", 10 out of 22 (45.45%) type "B", and"4 out of 22 (18.18%) type "C. At this point in the group of animals treated with insecticide the areas commonly parasited by the horn fly (flanks and back) a few lesions or no lesions were depicted whereas in the group of non-treated animals those areas were almost totally covered by lesions. After the total tanning the classification was 40.90% of type "A" leather, 50% type "B" and 9.09% type "C". This change was chiefly due to a process called make up, used to remove all marks. It must be emphasized that the leathers had lesions from other parasites such as Dermatobia hominis and Boophilus microplus and lesions acquired in the slaughter house as well. The results suggest that the horn fly does not present a real economic loss to the leather industry.
lesions; horn fly; leather; bovine