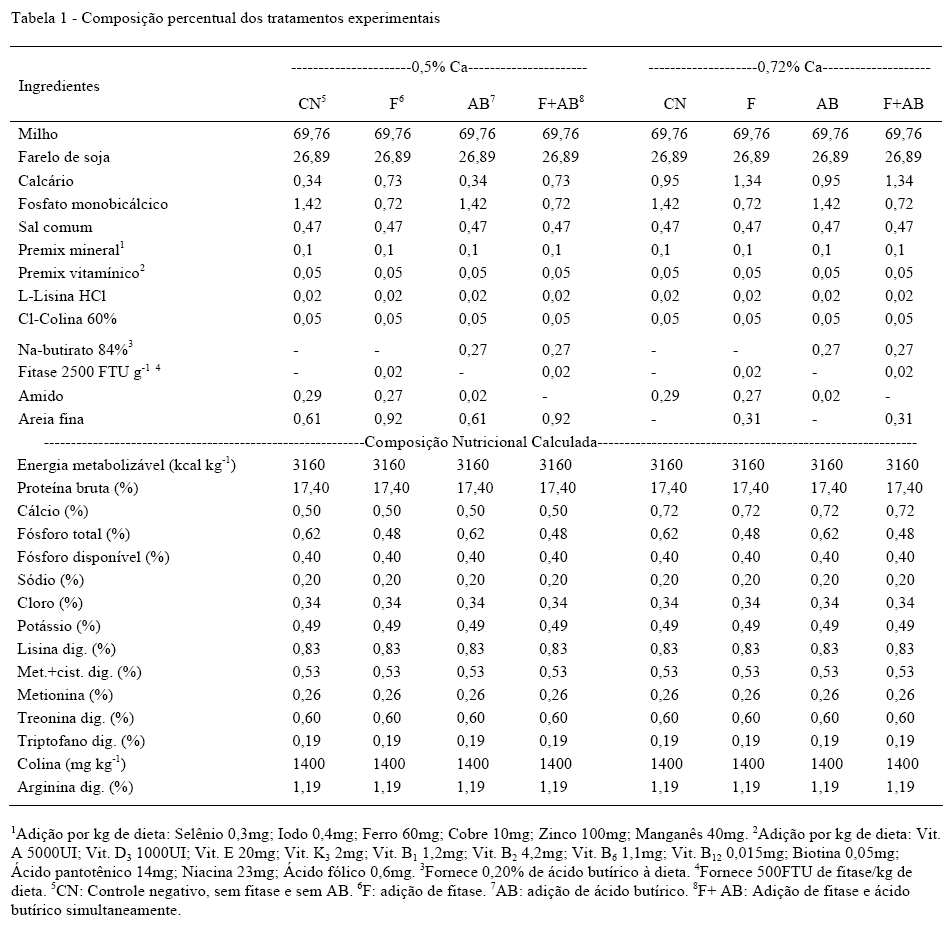
It was studied the use of butyric acid (BA) and phytase in growing pigs diets, varying calcium level. The experiment was divided into two periods of time, of 17 days, with 3 days of adaptation and 14 of measurements. In each period, it was used 16 barrows weighing 24.6±0.7kg in the first and 43.2±1.77kg in the second. Diets were different in calcium level (0.5 or 0.72%), AB (0 or 0.3% sodium butyrate 84%) and phytase (0 or 500FTU kg-1 phytase of bacterial origin derived from Escherichia coli). The experimental design was in randomized blocks (periods), decomposed in 2x2x2 factorial, with four replications. It was evaluated the apparent digestibility of nutrients, gross energy and balance of Ca and P. AB improved crude protein digestibility, but individually or in combination with phytase did not increase minerals retention. Phytase increased P retention by reducing urinary and fecal excretion. The lowest diet calcium level provided higher Ca retention and lower P retention as a result of increased P excretion in urine (P<0.0001). Despite improving protein digestibility, AB did not increase mineral retention and didn't have an additive effect with the use of phytase, while phytase had positive effect on retention of P.
acidification; calcium; enzymes; phosphorus

 Nutrient digestibility and Ca and P balance in pigs receiving butyric acid, phytase and different calcium levels
Nutrient digestibility and Ca and P balance in pigs receiving butyric acid, phytase and different calcium levels