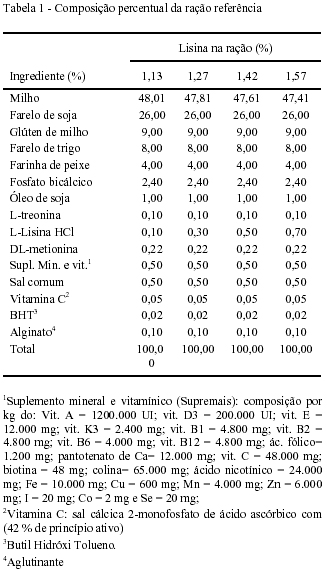
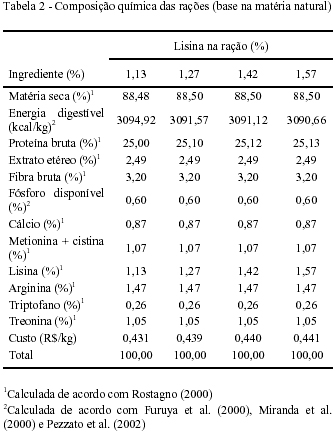
The present study was carried out to determine the lysine requirement for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Seventy two reversed fish with average weight initial of 117.9 ± 0.67g were for by 50 days with four diets (25% of crude protein and 3090kcal kg-1 of digestible energy) containing different values of inclusion of L-Lysine HCl: 0.1; 0.3; 0.5 and 0.7%, corresponding to rations with 1.13; 1.27; 1.42 and 1.57% of lysine, respectively. Fish were distributed in 12 tanks of 1000-L each, in a completely randomized design with four treatments, three replicates and six fish per experimental unit. No differences were observed in the temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen and electric conductivity of the water in the different treatments. No effects (P>0.05) of lysine inclusion were observed on survival rate, feed conversion, visceral fat, hepatosomatic index and carcass yield. There was no sign of quadratic effect (P<0.05) on weight gain and protein efficiency ratio, estimating the requirements values of 1.42% (5.7% of crude protein or 4.8mg of lysine kcal-1 of digestible energy in diet) and 1.35% of lysine (5.4% of crude protein), respectively. Considering the performance, a requirement value of 1.42% of lysine (5.7% of protein or 4.8 mg of lysine/kcal of digestible energy in diet) was obtained for Nile tilapia, in grow-out phase.
lysine; Oreochromis niloticus; performance; requirement; termination

 Lysine requirement of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), for grow-out phase
Lysine requirement of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), for grow-out phase