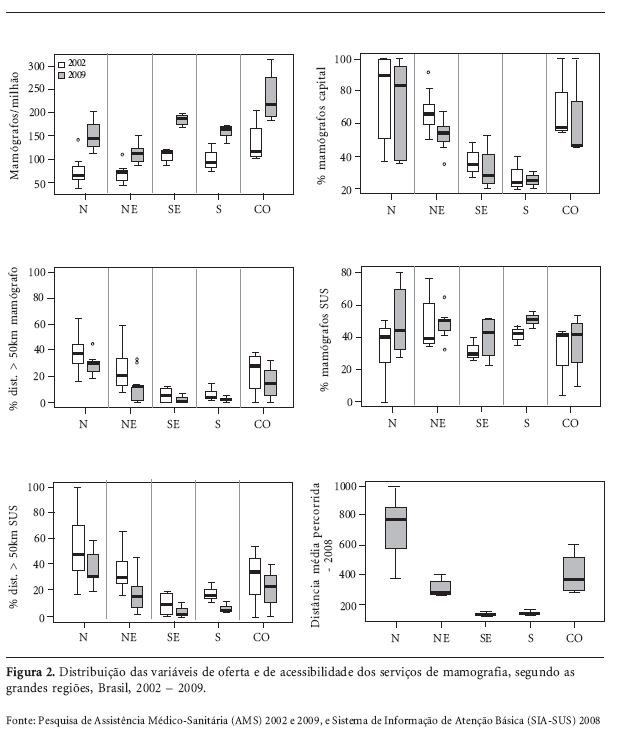
This study examined the effect of population characteristics and geographic location of residences and services on the odds of receiving a mammography in 2003 and 2008. Patterns of mammography use were analyzed using data from the Health Supplements of the National Household Sample Survey for women aged over 25, using prevalence ratios, and for women over 40 using multivariate logistic regression, correcting for complex sample design effects. In 2003, 54.6% of women of 50-69 years of age reported having had a mammography, in 2008, 71.5%. The odds are higher for those 50 to 69 years old, and increase with family income, education, being married, having consulted a doctor and having health insurance. Living in a metropolitan area trebles the chance of mammography. Compared to the Northern region, residents in all other regions have greater odds, greater distances decrease the odds. Coverage increased in the age range targeted by national policy, and inequalities due to income and education on access to mammography were reduced but regional convergence was not marked. Increased access seems to relate more to policies of income distribution and social inclusion, and to the availability of the examination in the Unified Health System, than to an increasing number of mammography units.
Breast cancer; Mammography; Health service accessibility; Information Systems