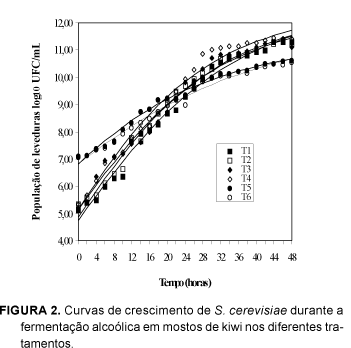
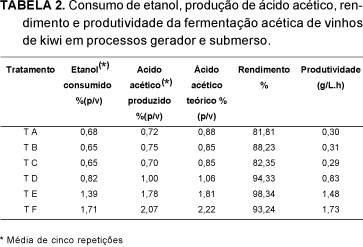
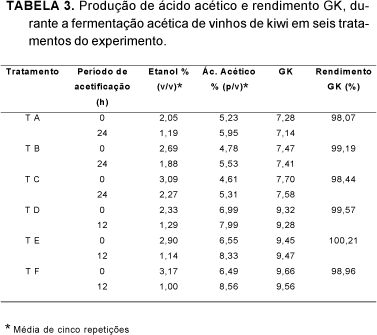
The kiwi culture has been expanding and the production of vinegar is an alternative that aims to use surplus fruits to diversify production. In this study, kiwi fruit (Actinidia deliciosa) vinegar was produced using submerse and generator methods. Mashes were prepared in six treatments: natural kiwi fruit juice (T1); kiwi fruit juice and nutrients added (T2); kiwi fruit juice and sucrose until 18O Brix (T3); kiwi fruit juice and sucrose until 18O Brix and nutrients (T4); kiwi fruit juice and sucrose until 22O Brix (T5); and kiwi fruit juice and sucrose until 22O Brix and nutrients (T6). The alcoholic fermentation occurred at 28O C, with 10(6) CFU/mL of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Only treatments 1, 3 and 5 were used in the acetic fermentation since the addition of nutrients didn't influence ethanol production. In acetic fermentation vertical generator (PG), at room temperature, and submerged fermentator (PS), at 25O C, 500rpm agitation an oxygen flow of 0.05vvm, both in a 2-liter work volume were utilised. The alcoholic fermentation yield varied between 38.65 and 47.23%, with efficiency of 75.62 to 92.41% and it's productivity between 0.74 and 2.0g/L.h. The pH values were higher at the end of the process in treatments with lower concentrations of total sugars (T1 and T2). In acetic fermentation at the PG, the composition of mashes didn't increase acetic acid production, but for PS initial higher concentrations of ethanol were more productive. The vinegars obtained by PS, produced in 12 hours between 1.00 and 1.78% (p/v) acetic acid, with yields varying between 93.24 and 98.34% and productivity between 0.83 and 1.73g/L.h. The sensory analysis performed with a ranking test showed that kiwi fruit vinegars obtained by PG were better than those obtained by PS, with acceptability indexes above 70%. The analyzed data showed that it is possible to produce kiwi fruit vinegar using surplus production fruits to diversify the products.
Actinia deliciosa; vinegar; fermentation; mashes composition; production methods