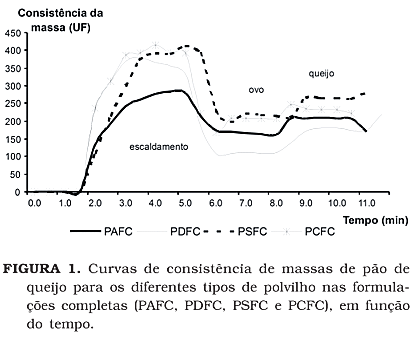
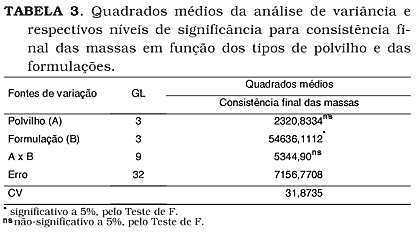
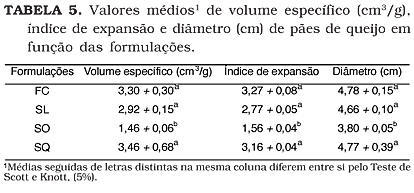
The process of production cheese bread involves scalding of the cassava starch with milk, water and oil, kneading with egg, addition of cheese and baking. This work had as objective to study the function of the ingredients in the consistency of the dough and in the characteristics of the produced cheese breads. The doughs were obtained of 100% sour starch (PA), 100% sweet starch (PD), 70% sour + 30% sweet (PS) and 50% sour + 50% sweet (PC), combined with the following formulations: with all the ingredients (FC), without milk, but with water (SL), no egg (SO) and no chesse (SQ). The doughs were developed in Farinograph Brabender and the evolution of their consistency were accompanied by graphs. The doughs were molded and baked and the characteristics of the breads cheese were analyzed. It was observed an increase of the consistency values during the scalding and mixture, the egg caused drastic fall of this consistency while the cheese an elevation, turning the dough moldable. The consistency of the doughs were more affected by the formulation and the without milk formulations (SL) presented the highest values; the without chesse formulations (SQ) presented lowest consistency. The doughs without egg (SO) were dry, hard, being cut into pieces when handled. Cheese breads FC and SQ presented high specific volume and larger diameter. Cheese breads SO presented smaller expandion index. The egg and the cheese played important role in the obtaining of doughs moldable easily, originating cheese breads with good structural characteristics.
cheese bread; ingredients; consistency of the doughs; physical characteristics