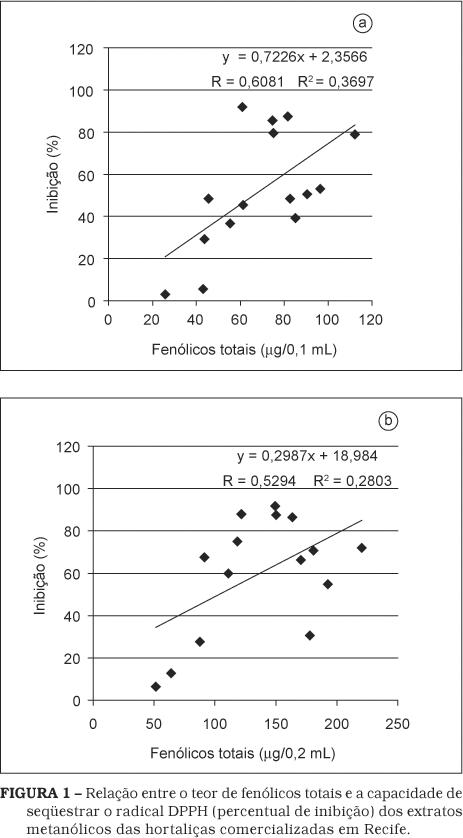
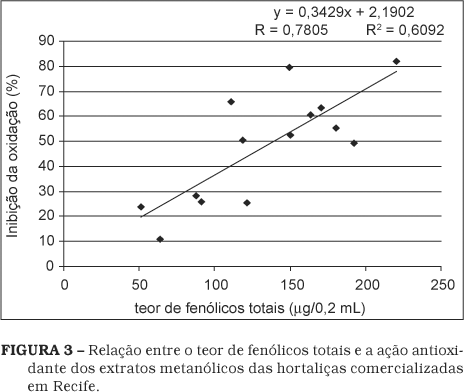
This study was carried out to determine the antioxidant capacity of 15 vegetables commonly consumed in Recife - PE, Brazil. Methanol extracts were screened for their antioxidant activity using two tests: DPPH free radical scavenging and beta-carotene/linoléico acid assay. All vegetables showed antioxidant properties however the action was differentiated among the kinds of vegetables. The methanol extracts of collard greens, tomatoes, potatoes, cauliflowers, green cabbage, spinach and lettuce "crespa" had the highest percentage in terms of free radical scavenging activities (> 70%). A moderate activity (60-70%) was shown by lettuce "lisa", white onion and green beans while purple onion, chayote, cucumber and carrot had the lowest free radical scavenging activities. In the beta-carotene/linoleic acid assay, spinach and collard greens extracts showed strong antioxidant activity (> 70%). The lettuce "lisa", white onion and cauliflower had a moderate action (60-70%) while the chayote, carrot, cucumber, tomato and green bean showed weak antioxidant activity. The results indicate that vegetables which were evaluated may provide a source of dietary antioxidant therefore their consumption must be encouraged.
vegetables; antioxidant action; DPPH; beta-carotene/linoleic acid model system

 Antioxidant capacity of vegetables commonly consumed
Antioxidant capacity of vegetables commonly consumed