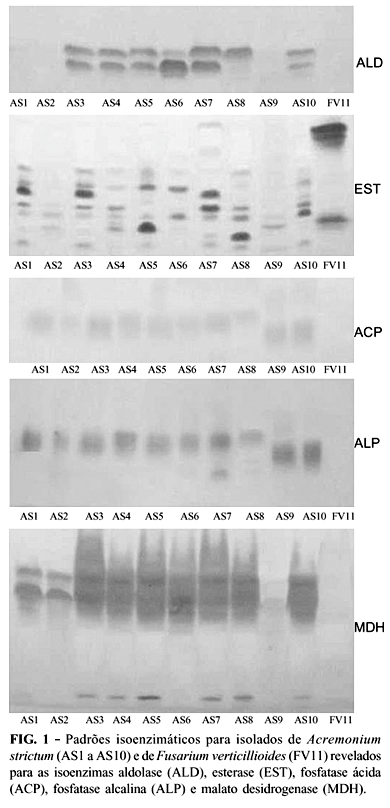
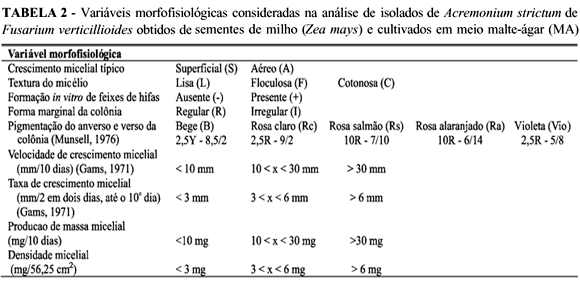
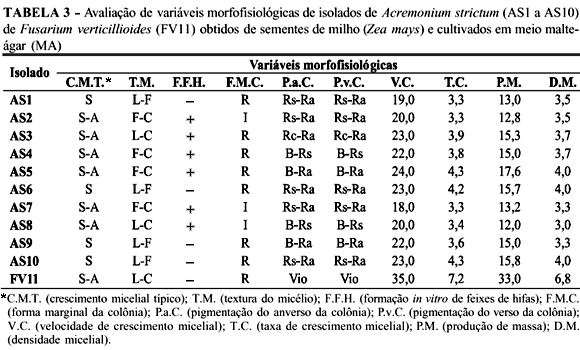
Differentiation between Acremonium strictum and Fusarium verticillioides in corn (Zea mays) seeds is very difficult because they present morphological similarities. Isoenzimatic analysis has been applied with success, allowing the development of fast, sensible and specific methods for diagnosis of plant pathogens in complement to morphological analysis. The objectives of this work were to characterize and evaluate the genetic diversity of ten isolates of A. strictum associated with corn seeds from different Brazilian regions by means of morphophysiological and isoenzymes analysis, in comparison to one isolate of F. verticillioides. Nine morpho-physiological characteristics and five isoenzymes systems (aldolase, esterase, acid phosphatase, alcalin phosphatase and malate dehydrogenase) were considered in this study. Isoenzymatic analysis produced 28 polymorphic bands. Colony pigmentation, growth rates, weight, mycelial density and isoenzymatic analysis were efficient for grouping A. strictum isolates and to distinguish them from F. verticillioides. The isolates of A. strictum showed variable intraspecific diversity between 0% to 89,5%. No phenotypic similarities were correlated with geographic origin of the A. strictum isolates.

 Morphophysiological and isoenzymatic markers in a genetic diversity analysis of Acremonium strictum isolates
Morphophysiological and isoenzymatic markers in a genetic diversity analysis of Acremonium strictum isolates