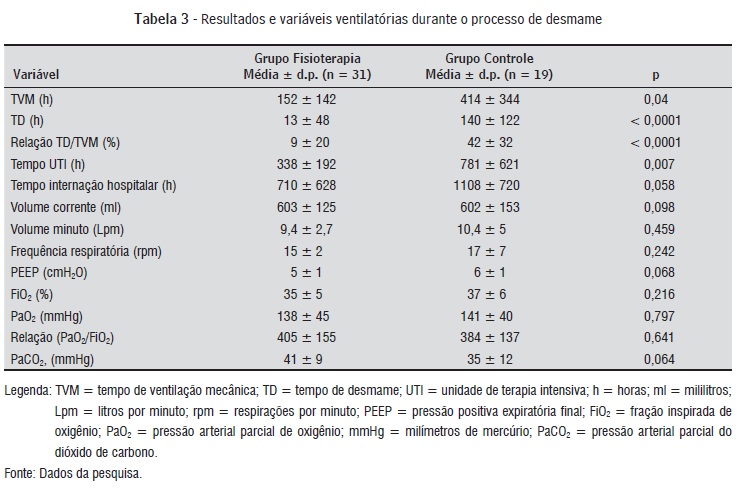
INTRODUCTION: Physiotherapy is acting with the aim of reducing failures in weaning from mechanical ventilation (MV), which may impact on unfavorable outcomes. OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the effects of physiotherapy in weaning from MV. MATERIAL AND METHODS: This transversal and controlled study included adult patients. During the duration of the study, for administrative reasons, the ICU has gone through a period without physiotherapy. Daily information was collected from medical records on the outcome of weaning from MV. We studied 50 patients, 31 aided by physiotherapy (physiotherapy group, PG) and 19 without physiotherapy (control group, CG). The PG underwent two sessions daily (forty minutes each). The techniques applied were: chest compression, manual hyperinflation, tracheal and upper airways suctioning, movement and conduct of monitoring and weaning. RESULTS: The results of weaning in PG and CG are respectively: successful weaning: 71% (22) and 21% (4) (p = 0.001), duration of MV: 152 ± 142 and 414 ± 344 hours (p = 0.04), duration of weaning: 13 ± 48 and 140 ± 122 hours (p < 0.0001), length of ICU: 338 ± 192 and 781 ± 621 hours (p = 0.007), length of hospital: 710 ± 628 and 1108 ±720 hours (p = 0.058), mortality 35% (11) and 47% (9) (p = 0.41). CONCLUSION: The physiotherapy in the ICU was associated with increase of the success rate, reducing weaning time, duration of MV, length of stay in ICU. There were no differences in length of hospital stay and mortality.
Ventilator weaning; Respiration artificial; Physical therapy specialty