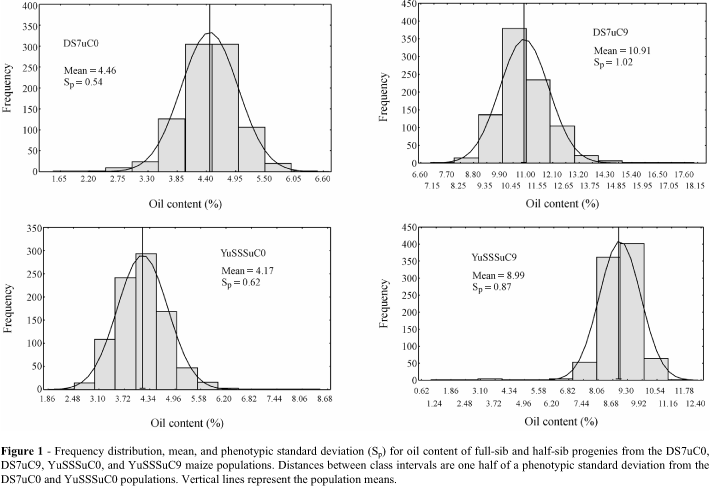
The objectives of this study were to estimate changes in oil content, grain yield, percentage of broken plants and changes in yield components in the maize populations DS7u and YuSSSu. As estimations were performed at C0 and C9 for both populations, it was possible to observe changes occurring following long-term mass selection for high oil content. The synthetic population DS7u population was developed by recombination of 29 inbred lines of Yugoslav, Canadian and US origin. The synthetic population YuSSSu population is an Iowa Stiff Stalk Synthetic - BSS(R)C5. Progenies were derived according to the North Carolina Design II. Results indicated that nine cycles of selection led to statistically significant increase in oil content and statistically significant decrease for grain yield in both populations. Estimates of additive and dominance variances for grain oil content were highly significant in C0 and C9 of the population DS7u population. Dominance variance showed significance in the initial cycle of the population YuSSSu population, but it was not detected in the course of nine cycles of mass selection. Additive and dominance variances for grain yield were highly significant in both initial populations. Loss of significance did not result from selection, while the proportion of dominance vs. additive variance became greater. High narrow-sense heritability was detected for grain yield, oil content, moisture content, and cob percent in the initial cycles of both populations. Mass selection resulted in increased heritability for oil content and cob percent in the DS7u population and increased heritability for percentage of broken plants in the YuSSSu population. The strongest additive correlation between oil content and other traits was detected for grain moisture (r a = 0.90*) in the C9 of the DS7u population.
corn; mass selection; high oil populations; components of genetic variance; additive and phenotypic correlations