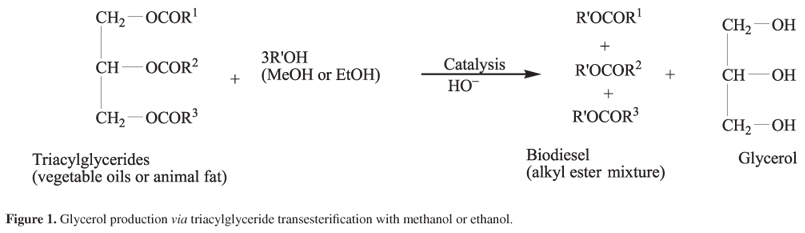
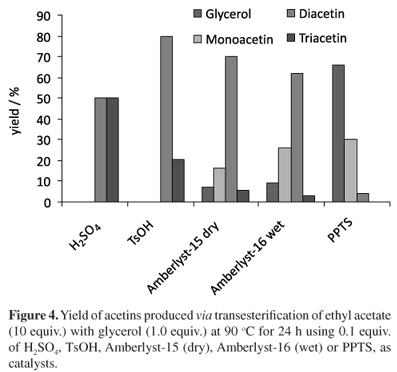
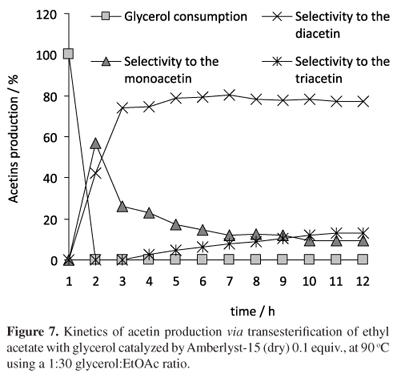
A new catalytic route with potential practical interest to sustainable production of bio-additives from glycerol is described. Ethyl acetate was transesterified with glycerol, in the ratio glycerol:EtOAc 1:10, at 25 or 90 ºC using 0.1 equiv. of H2SO4 or TsOH, as homogeneous catalysts. H2SO4 led to the total glycerol consumption in 2 h. In the equilibrium, attained in 9 h, 100% yield of a diacetin:triacetin (55:45) mixture was formed. Using AmberlystTM 15 dry and AmberlystTM 16 wet in 1:30 glycerol:EtOAc ratio and reflux at 90 ºC the total glycerol consumption was achieved in 2 and 10h, respectively. The lower reactivity of Amberlyst-16 wet was explained in terms of deactivation of acid sites and decrease in glycerol diffusion to the inner resin pores, both factors caused by adsorbed water. The kinetics of glycerol transformation and product distribution in the equilibrium in relation to the H2SO4, Amberlyst-15 (dry) and Amberlyst-16 (wet) catalyzed reactions were measured.
triacetin; diacetin; Amberlyst-16 wet; acidic ion-exchange resins; glycerol acetylation