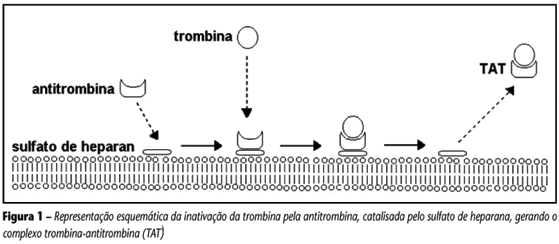
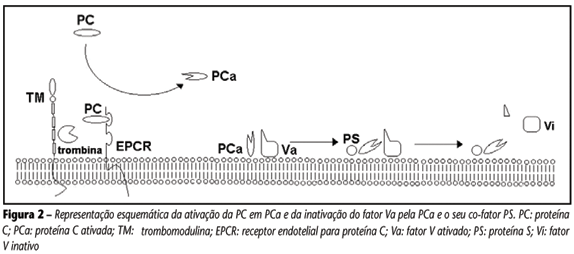
BACKGROUND: Hemostatic abnormalities have been associated with vascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (DM2). Efficiency of the natural anticoagulation mechanism mediated by proteins C (PC), S (PS) and antithrombin (AT) depends on intact endothelial cells, so the evaluation of these proteins may contribute to a better understanding of the natural anticoagulation status, considering that they inhibit the state of hypercoagulability. OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to measure AT, PC and PS levels and the cofactors, factors V (FV) and VIII (FVIII), in subjects with and without DM2 and hypertension (HAS). MATERIAL AND METHOD: 16 healthy subjects (controls), seven patients with DM2, 12 with hypertension (HAS) and 18 with DM2 associated to HAS (DM2 + HAS) were included in this study for natural anticoagulation evaluation. RESULTS: HAS group showed increased levels of AT compared with controls. DM2 + HAS group showed increased levels of PC. For PS and FVIII, no difference was observed among groups. Nevertheless, the increase of FV was observed in DM2 + HAS group, while DM2 group did not show increase. CONCLUSION: AT increase is not yet well known for all conditions. Previous studies have already described PC increase in normoalbuminuric patients with DM2, however its cause is also unknown. FV increase observed in DM2 + HAS group suggests that HAS should contribute to this increase. As FVIII is an acute phase protein the data for FVIII may indicate that assessed subjects had no important inflammatory condition.
Type 2 diabetes; Protein C; Protein S; Antithrombin; Anticoagulation; Factor V; Factor VIII