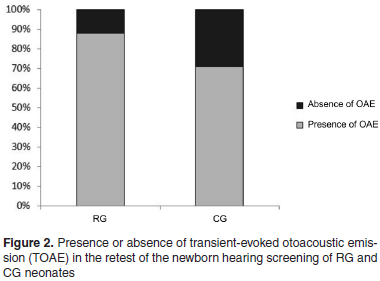
PURPOSE: To analyze the otoacoustic emissions (OAE) of the newborn hearing screening of infants born to HIV-seropositive mothers. METHODS: It was carried out the Transient-Evoked OAE and the research of cochleopalpebral reflex in 247 full-term newborns with no risk factors for hearing. The Control Group (CG) comprised 167 infants, and the Research Group (RG), 80 infants that had been exposed to HIV during gestation. It was considered "failure" when the newborn had absence of TOAE in at least one ear. Data were statistically analyzed. RESULTS: In the, Eight infants (10%) from the Research Group and seven (4.2%) from the Control Group failed in the newborn hearing screening (p=0.09). Retest of the infants who failed showed persistence of the absence of OAE in one subject (12.5%) from the Research Group and two (28.6%) from the Control Group (p=0.6). Cochleopalpebral reflex was present in all subjects. CONCLUSION: There was no association between the absence of TOAE and the newborn's HIV exposure during gestation.
Ear, inner; Neonatal screening; HIV seropositivity; Hearing; Hearing disorders; HIV infections