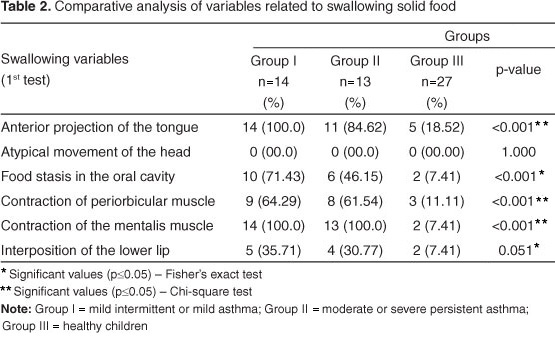
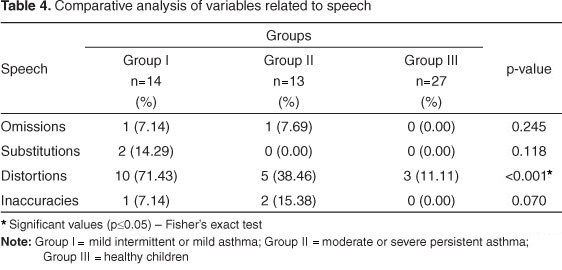
PURPOSE: To compare the orofacial functions (chewing, swallowing and speech) in children with asthma and healthy children. METHODS: A cross sectional study including 54 children of both genders with ages between 7 and 10 years was conducted. Twenty-seven of these subjects composed the experimental group, and were subdivided into two severity levels of asthma: Group I - mild intermittent and persistent asthma; Group II - persistent moderate to severe asthma. Twenty-seven healthy children were included in the control group (Group III). Speech-language pathology evaluation used the adapted Orofacial Myofunctional Assessment Protocol. Adaptation consisted in the exclusion of the structural part of the test, since this was not the aim of the study. The structural part was excluded because it was not the aim of this study. RESULTS: It was found alterations in oral functions, with significant differences between the three groups. These alterations showed no correlation with asthma severity, since the highest rate of alterations was found in Group I (mild asthma). CONCLUSION: Regardless of the severity level, children with asthma have altered patterns of chewing, swallowing and speech.
Stomatognathic system; Asthma; Mastication; Deglutition; Articulation disorders; Child