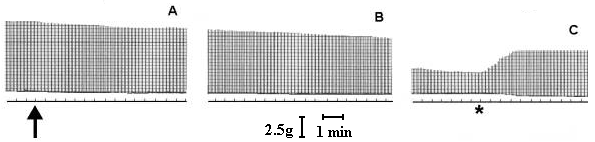
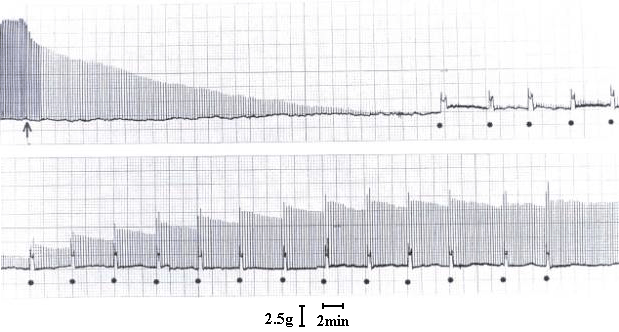
In 1919, Houssay and Negrete reported that venoms of Theraphosidae spiders induced neuromuscular blockade. In 1993, a purified toxin from Grammostola spider venom was found to block the P-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC), causing neuromuscular blockade. We studied the mode of action of Theraphosa blondii venom, a large Theraphosidae spider from Northern Brazil, Venezuela, and The Guyanas in mouse phrenic nerve-diaphragm preparation. This venom elicited a partially reversible neuromuscular blockade and did not depress directly evoked twitches or alter the membrane potential. Neostigmine produced only a poor antagonistic effect on partially blocked diaphragms. However, completely blocked miniature endplate potentials (m.e.p.ps) were reverted by neostigmine. These results can be explained by the presence of toxins in the venom that interact with the endplate receptor at the acetylcholine sites (curaremimetic toxins) and toxins that inhibit the P-type voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC) (omega -toxins). This study shows that Theraphosidae venoms, especially those of the Theraphosa blondii, are a source of curaremimetic toxins and omega -toxins of possible interest as tools in bioscientific research.
spider venom; mouse diaphragm preparation; neuromuscular junction; Theraphosa blondii