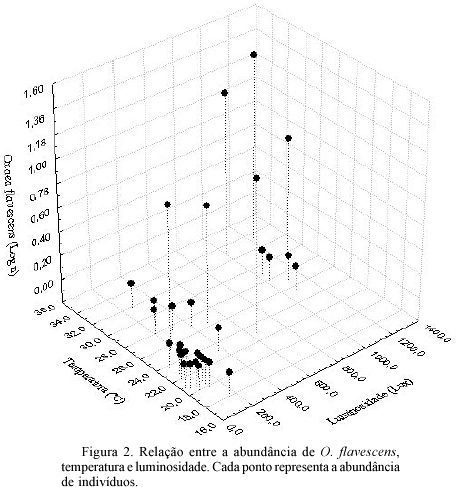
The influence of abiotic factors and floral resources on the frequency of insect visitors to Stachytarpheta glabra Cham was assessed in an area of ferruginous fields, Ouro Preto, MG. A total of 312 insects were collected, belonging to 28 species. The highest abundances were for Oxaea flavescens Klug (25%), Vespidae sp1 (11.5%), Vespidae sp2 (11%), Antheos clorinde Hubner (10.3%) and Vespidae sp3 (10%). There was a positive relation of abundance with light intensity (r² = 0.66, b = 0.82, P < 0.001) and temperature (r² = 0.40, b = 0.65, P = 0.001), and a negative relation with relative humidity (r² = 0.34, b = -0.60, P < 0.001). The number of flowers and inflorescences (rS = 0.81, n = 20, P < 0.001 e rS = 0.82, n = 20, P < 0.001, respectively) influenced the abundance of visits. No significant relation was found with plant height. Halictidae prefer to forage at high temperatures and light intensity. Large bees (Apidae and Andrenidae), on the other hand, are more tolerant to temperature variations and forage during the whole day. Vespidae prefer high temperatures but tolerate variation in light intensity. Lepidoptera forage preferentially during periods of high light intensity and temperature. Butterflies, moths, Eulaema nigrita Lepeleier and Apis mellifera L. are the potential pollinators whereas Vespidae, Halictidae, Bombus atratus Franklin and O. flavescens were thieves in S. glabra flowers.
Pollinator; resource partition; abiotic constraint