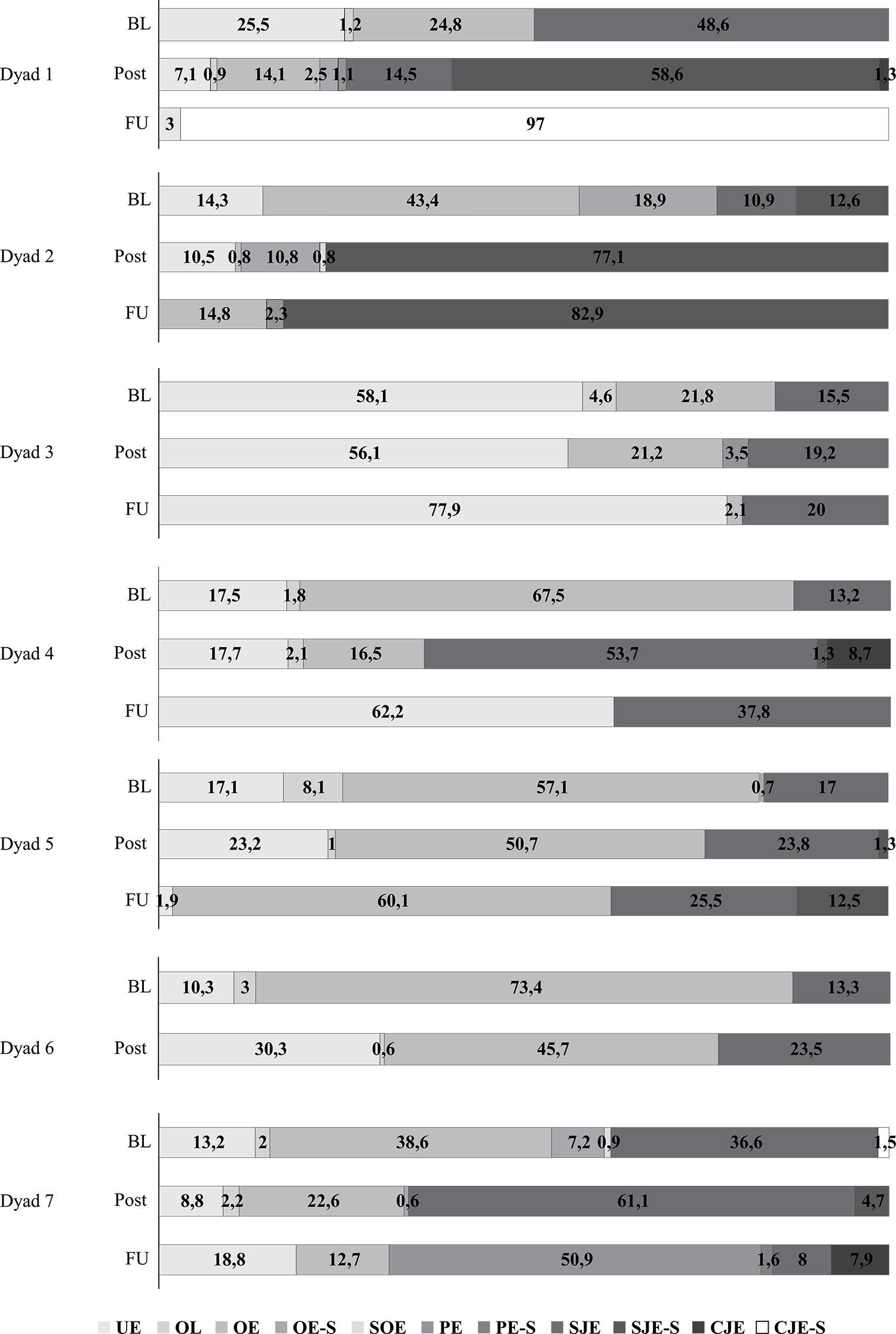
To become involved in states of social engagement with their caregivers is a core deficit of children with autism. This study verified the effectiveness of an intervention with caregivers for the promotion of social engagement in their children with autism. The interactions of seven dyads were video recorded before, during and after the intervention in order to record the duration of eleven states of the children’ attention engagement, coded as social engagement (SE) or non-social engagement (NSE). Eight hours of intervention were divided into meetings with all the caregivers and into individualized monitoring. After the intervention, significant differences were observed regarding the increase of SE and in the decrease of NSE and these gains were maintained at follow-up. The increase in SE was positively associated with the degree of caregivers’ adherence to the treatment. We conclude that short duration interventions can qualify caregivers as competent mediators to increase social engagements.
autism; social interaction; caregivers