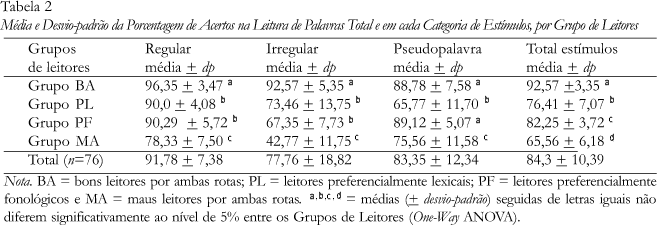
Multiple interdependent processes compose the reading. The present study analyzed the preferential usage on one of the reading routes (Dual Route Cognitive Reading Model) and the possible relations with reading comprehension and reading time in 76 children from second and third grades, in a Elementary private school. The reading of isolated words, comprehension and textual reading time were evaluated. Four groups were identified according with the skills of word reading: good readers in both routes (phonological and lexical), poor readers in both routes, preferably lexical readers and preferably phonological readers. The group of good readers in both routes was the fastest in textual reading. There weren't significant differences among the groups in reading comprehension, except in the third grade. It was concluded that both reading routes were functional in the sample, however the phonological route seems to be better developed than the lexical route, which is in expansion, suggesting a developmental process of the reading skills.
Reading; reading routes; reading comprehension; cognitive models