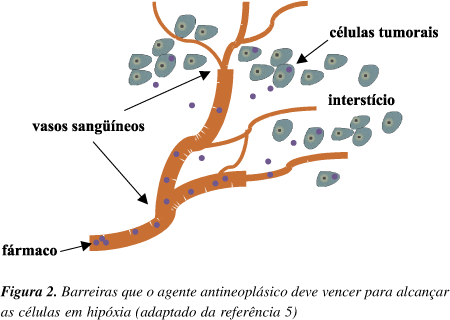
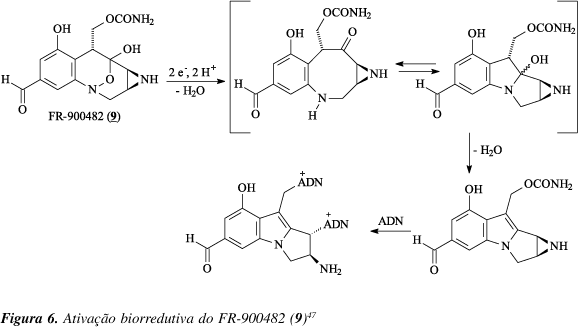
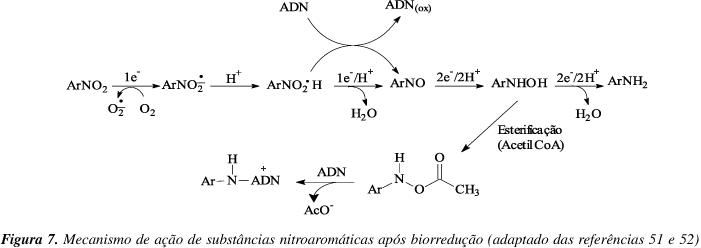
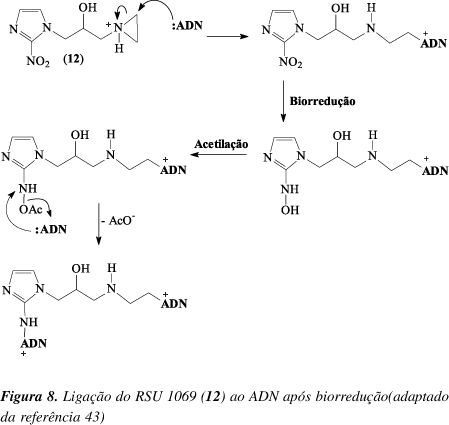
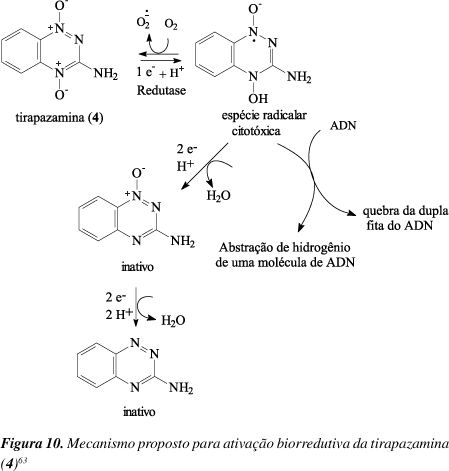
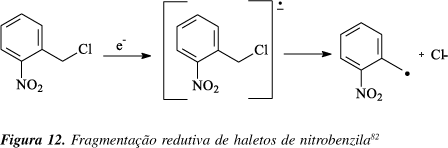
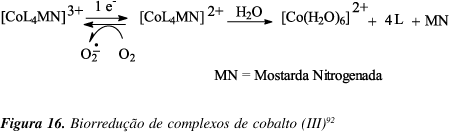
A problem often encountered in cancer therapy is the presence of tumor cell subpopulation that are resistant to treatment. Solid tumors frequently contain hypoxic cells that are resistant to killing by ionizing radiation and also by many chemotherapeutic agents. However, these hypoxic cells can be exploited for therapy by non-toxic hypoxic-activated prodrugs. Bioreductive drugs require metabolic reduction to generate cytotoxic metabolites. This process is facilitated by appropriate reductases and the lower oxygen conditions present in solid tumors. The unique presence of hypoxic cells in human tumors provides an important target for selective cancer therapy.
solid tumor; hypoxic cells; bioreductive prodrugs