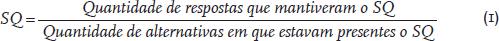ABSTRACT
In the context of the financial management of an organization, there are behavioral patterns that can bias the decision-making process, making the financial manager unable to achieve his/her goal of maximizing value in activities related to financial decisions, particularly those related to investments. One of these biases is called status quo. According to Samuelson and Zeckhauser (1988)Samuelson, W., & Zeckhauser, R. (1988). Status quo bias in decision making. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 1(1), 7-59., this bias indicates that individuals tend to maintain the current state of their portfolio and have difficulty in changing their financial position. This research examined whether there is a relationship between status quo bias, risk profile and quantitative skills in graduate studentsof economics, accounting, and management. For this purpose, a survey was conducted through questionnaires administered to 330 graduate students at the University of Porto (Portugal) and Federal University of Santa Catarina (Brazil). For the calculation and presentation of indicators that point to the presence of the status quo bias the methodology used was based on Samuelson and Zeckhauser (1988)Samuelson, W., & Zeckhauser, R. (1988). Status quo bias in decision making. Journal of Risk and Uncertainty, 1(1), 7-59.. In addition, a regression analysis was conducted to find a relationship between the risk profile of the participants and the status quo bias, including some control variables. The results showed that risk-seeker respondents seem to have been less affected by the status quo bias in their decisions, unlike the others. As for the participants who have studied behavioral finance in their undergraduate courses (a proxy for prior knowledge of the studied bias), it was found, on average, an increase of answers on alternatives to the status quo. However, the presence of the status quo bias was still dominant in the total responses. This shows that respondents who had studied behavioral finance opted for alternative options more than other respondents, but, even these individuals showed the status quo bias. Thus, we emphasize the importance of understanding the influence of behavioral biases in decision making, because these biases may impair important decisions within an organization.
KEYWORDS
Behavioral finance; Status quo bias; Risk aversion; Financial literacy; Endowment effect

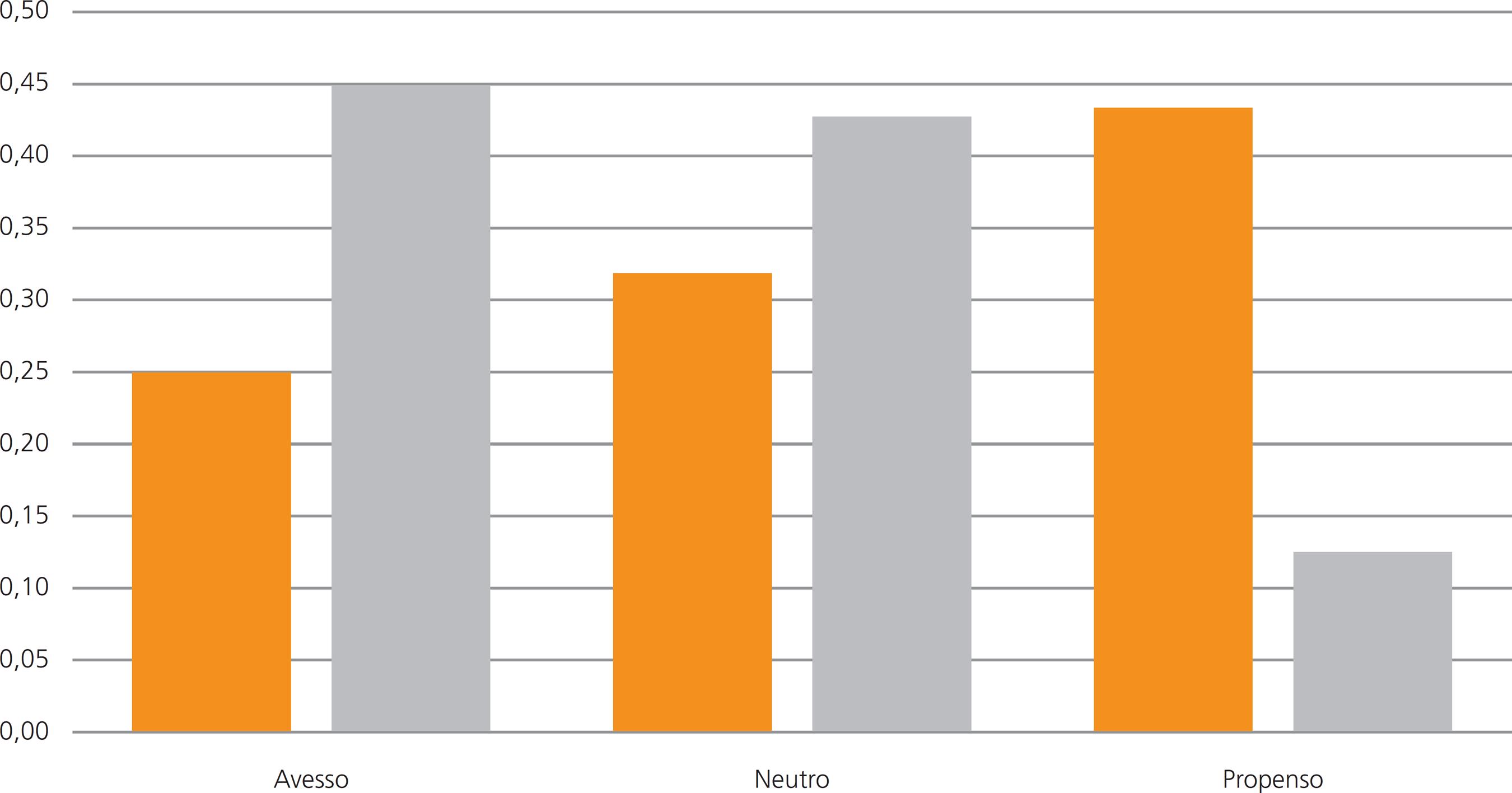 Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores.
Fonte: Elaborado pelos autores.