Abstract
Objective:
Hemodilution is a concern in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). Using a smaller dual tubing rather than a single larger inner diameter (ID) tubing in the venous limb to decrease prime volume has been a standard practice. The purpose of this study is to evaluate these tubing options.
Methods:
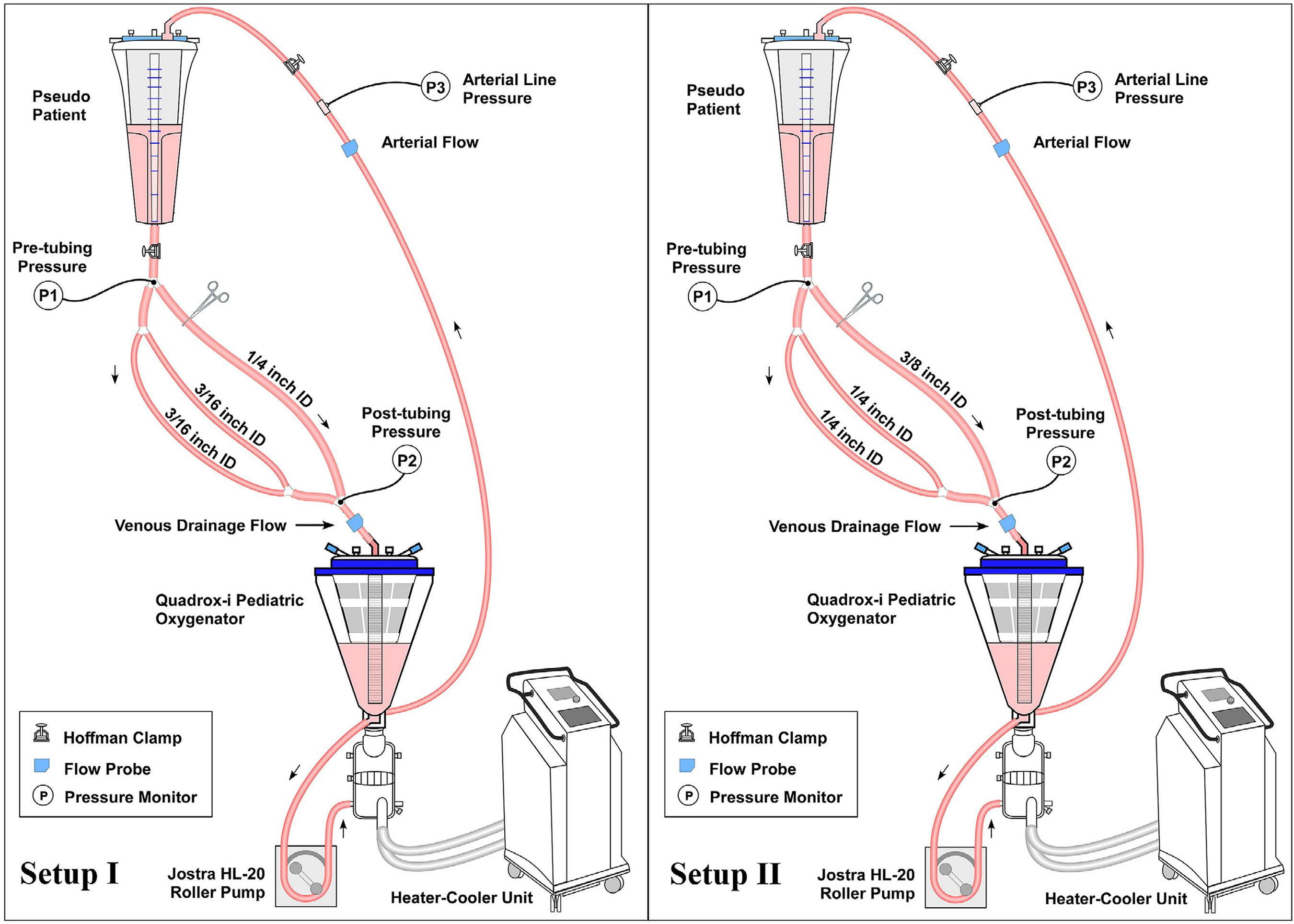
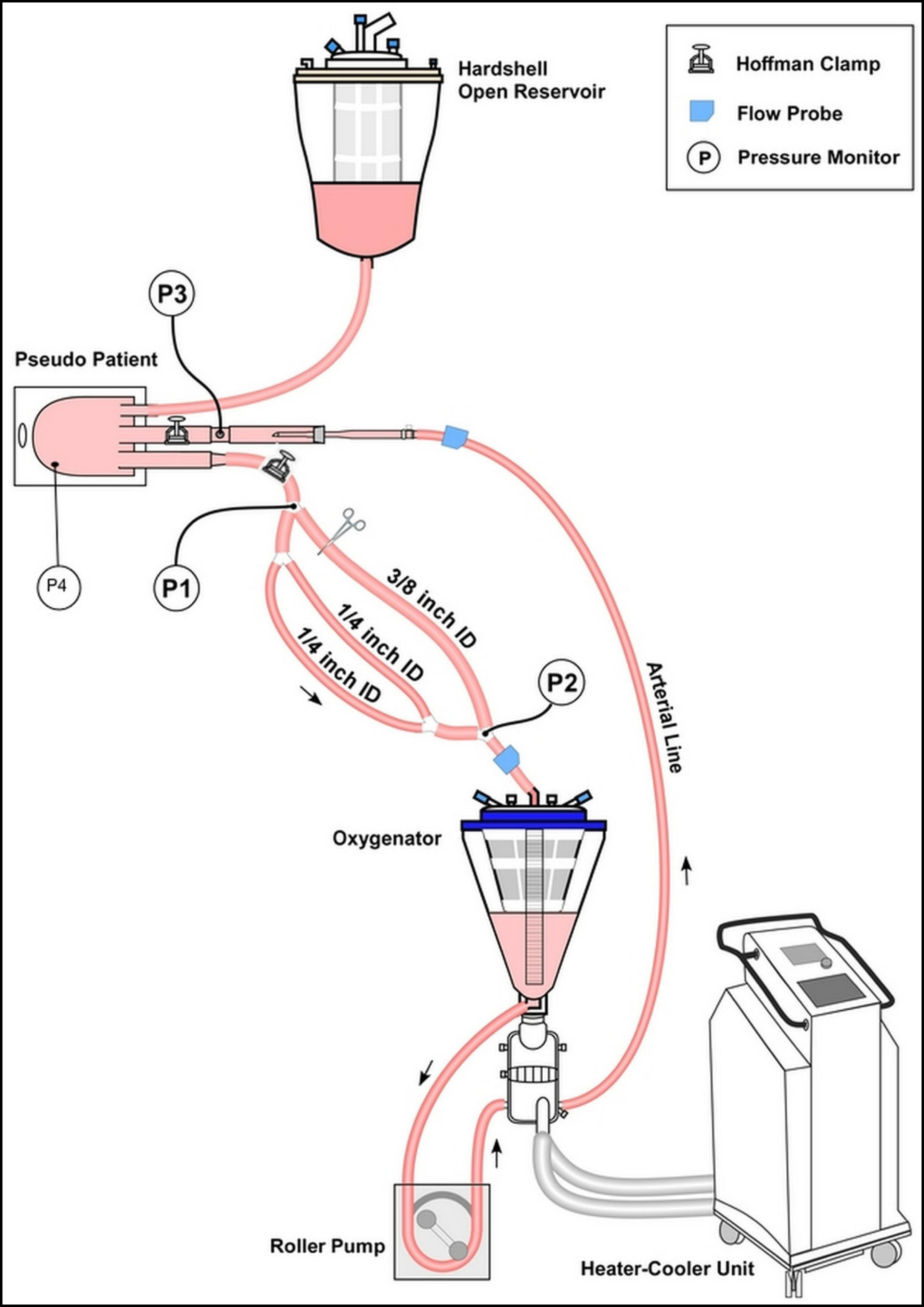
Four different CPB circuits primed with blood (hematocrit 30%) were investigated. Two setups were used with two circuits for each one. In Setup I, a neonatal oxygenator was connected to dual 3/16" ID venous limbs (Circuit A) or to a single 1/4" ID venous limb (Circuit B); and in Setup II, a pediatric oxygenator was connected to dual 1/4" ID venous limbs (Circuit C) or a single 3/8" ID venous limb (Circuit D). Trials were conducted at arterial flow rates of 500 ml/min up to 1500 ml/min (Setup I) and up to 3000 ml/min (Setup II), at 36°C and 28°C.
Results:
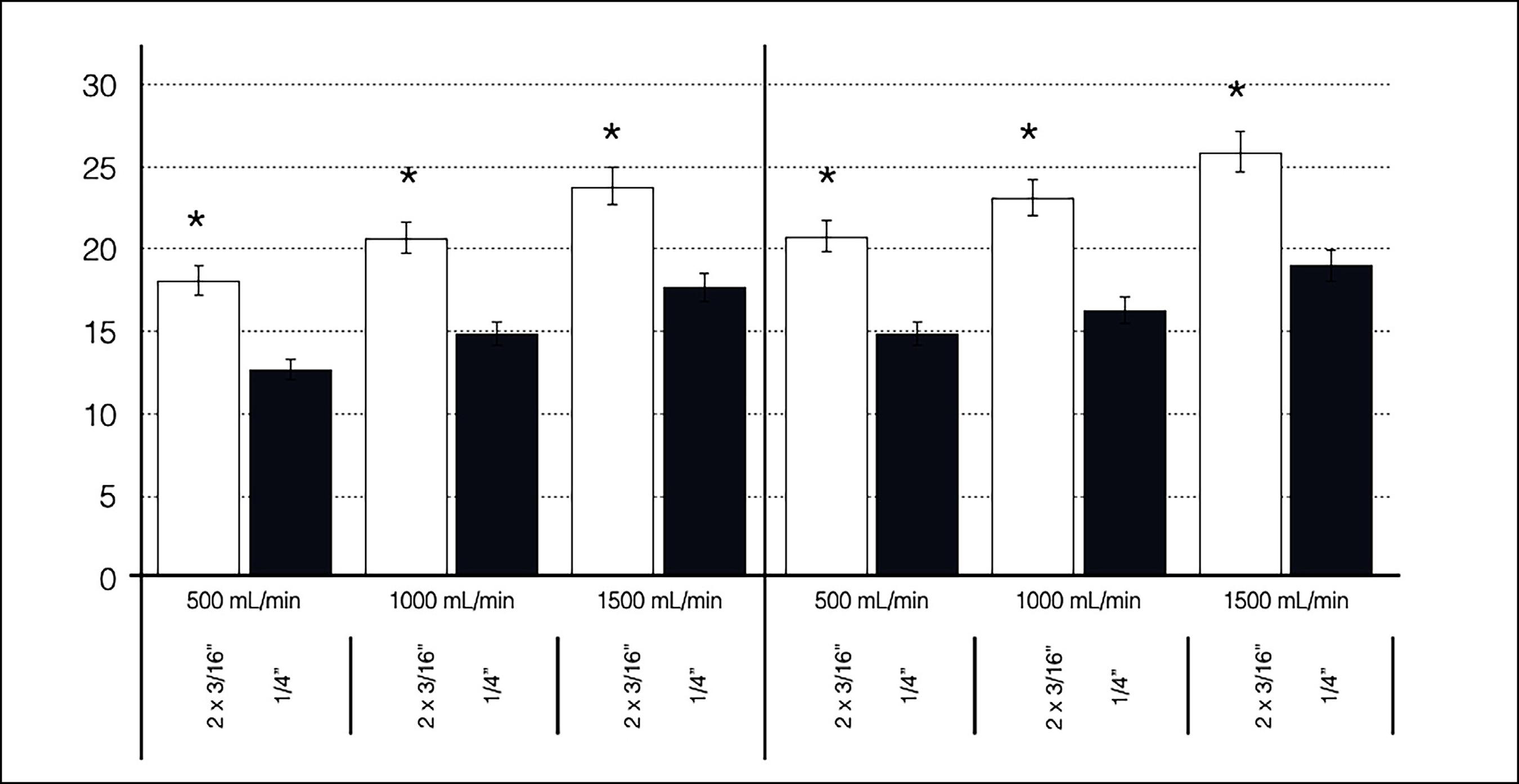
Circuit B exhibited a higher venous flow rate than Circuit A, and Circuit D exhibited a higher venous flow rate than Circuit C, at both temperatures. Flow resistance was significantly higher in Circuits A and C than in Circuits B (P<0.001) and D (P<0.001), respectively.
Conclusion:
A single 1/4" venous limb is better than dual 3/16" venous limbs at all flow rates, up to 1500 ml/min. Moreover, a single 3/8" venous limb is better than dual 1/4" venous limbs, up to 3000 ml/min. Our findings strongly suggest a revision of perfusion practice to include single venous limb circuits for CPB.
Keywords:
Cardiopulmonary Bypass; Pediatrics; Oxygenators; Membranes