Abstract
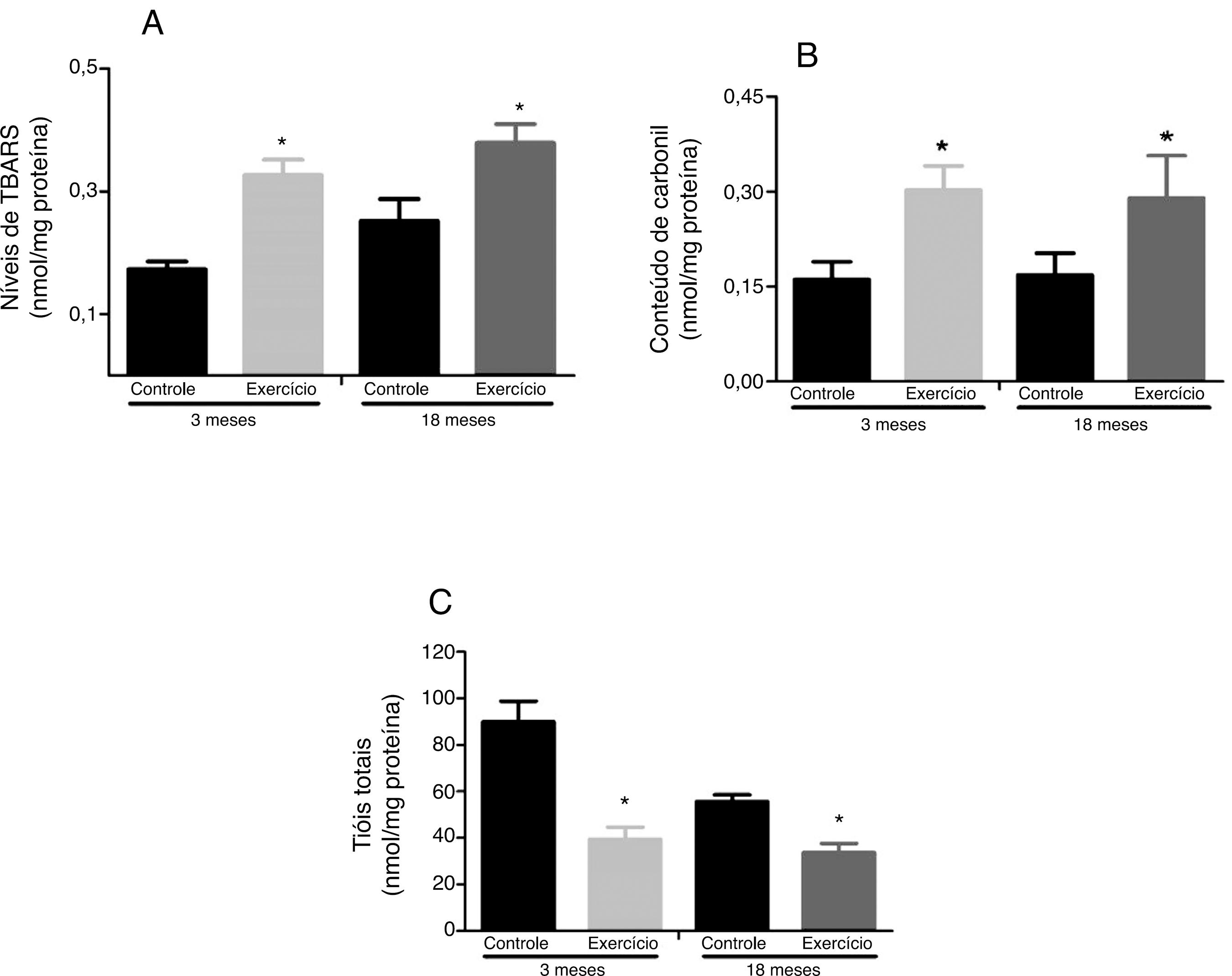
The effects of exercise on the generation of reactive oxygen species and the response to muscle oxidative stress determines longevity. This study compares the effects of acute exercise with similar relative workload in rats with 3 and 18 months. The animals were divided into four groups (n = 6): control 3-months; exercise 3-months; control 18-months and exercise 18-months. Exercised groups underwent to a single bout of running with 60 minutes in the speed 0.8 km/h (18 months) and 1.2 km/h (3 months). Metabolic parameters (lactate levels, glycogen content, succinate dehydrogenase levels, cytochrome c oxidase) and oxidative stress (activity of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase). The results showed an increase in metabolic markers after acute exercise regardless of the age and similarity in oxidative damage even if the antioxidant enzymes are age-dependent. These results suggest that the effects of acute exercise at moderate intensity, affects the metabolism independent of age, and, that the differential response in enzymatic antioxidant system between groups do not promote protection against oxidative damage.
KEYWORDS
Acute exercise; Aging; Oxidative damage; Oxidative stresso; Muscle