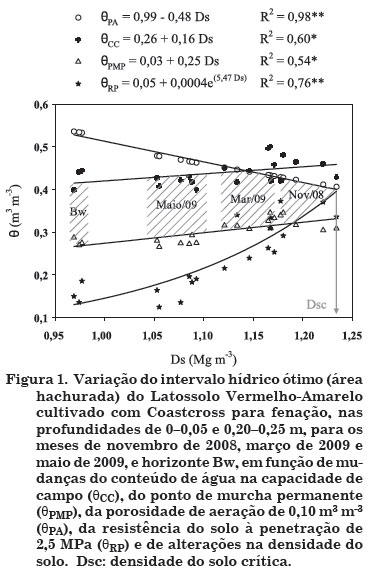
Grass pastures, if well-established and managed, play an important environmental role as soil cover, for aggregate formation and stabilization and in the reduction of dense or compacted layers. The objectives of this study were to quantify the least limiting water range (LLWR) of a physically degraded Red-Yellow Latosol (Oxisol) on which bermudagrass (Cynodon spp., cultivar coastcross) was planted, and to use the LLWR as an indicator of changes in the soil structural quality. Undisturbed samples were collected in volumetric rings (height 0.025 m, diameter 0.065 m) from the layers 0-0.05, 0.20-0.25 and 0.80-0.85 m (Bo horizon), in areas without machine traffic, during the rainy season of 2008/2009 in november 2008, march 2009 and may 2009. Based on these samples, the water retention curve, penetration resistance curve, bulk density, LLWR, and soil critical density were determined. The LLWR proved to be an adequate indicator of changes in the Latosol structure. The grass cultivar coastcross is potentially suitable for improving the soil structural quality, and is suggested for this purpose, instead of agricultural implements. The soil critical density of 1.24 Mg m-3 restricts the adequate development of the studied grass root system.
soil structural quality; water availability; soil resistance; soil physical quality