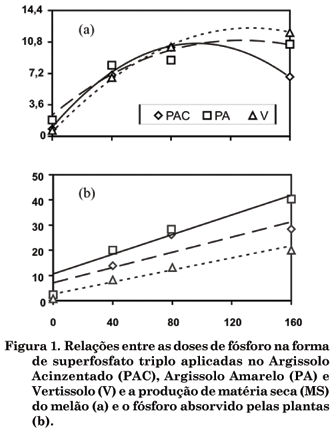
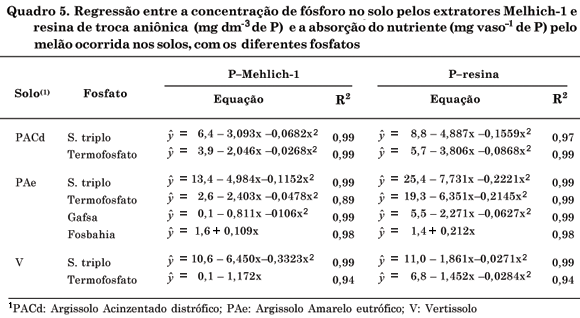
Organic agriculture is an emerging activity in the upper mid São Francisco River Valley, requiring technologies that are in line with the principles of this agricultural system. A study was carried out at Embrapa Semi-Árido to evaluate the efficacy of natural phosphates applied to three regional soils (dystrophic Grey Argisol - PAGd, eutrophic Yellow Argisol - PAe and Vertisol - V) planted with melon (Cucumis melo) in pots accommodated on wooden benches. The factorial treatments (3 x 4) + 1 consisted of three phosphorus levels (40, 80 and 160 mg dm-3 P2O5), four phosphorus sources (triple superphosphate-ST, thermophosphate-TM, Gafsa natural rock phosphate-FG and Fosbahia natural phosphate-FB) and a control treatment without phosphorus, in a completely randomized design with three replications. Each soil represented a trial. Shoot dry matter (DM), P plant content and P soil concentration extracted by Mehlich-1 and anionic exchange resin (AER) were evaluated 38 days after planting. In V and PAGd soils the phosphates were less effective than in PAe soil. TM was the P source with the highest efficiency for DM production in the three soils (56 to 100 % in relation to triple super phosphate). In PAe, FG also presented relatively high efficiency, equivalent to 80 % of that obtained with triple super phosphate. The Mehlich-1 and AER extractors were equally effective at evaluating P availability.
Cucumis melo; soil; phosphorus; chemical extractor