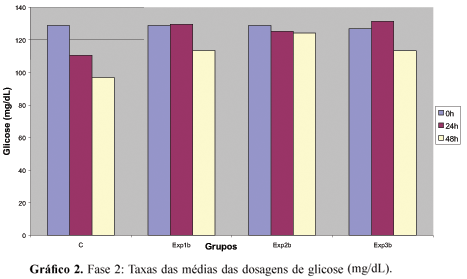
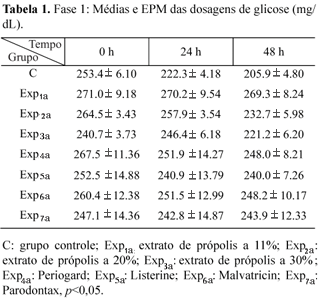
This study evaluated in vitro and ex vivo, the action of propolis extracts in different concentrations, in comparison with the effectiveness of oral antiseptics, against microorganisms present in human saliva. For in vitro experiences, glucose 25% solution was added to saliva, then individual samples were collected to prepare a control group (C) and experimental groups (Exp), with addition of propolis extracts in 11%, 20% and 30%, and extracts of Periogard, Listerine, Malvatricin e Parodontax. For ex vivo experiments, samples of saliva in fast and after mouthrinses with extracts of propolis 11%, 20% and 30% were collected and later glucose solution was added. In both phases of the experiments, successive samples of the mixtures were collected and glucose consumption by microorganisms present in human saliva was determined by the glucose oxidase method in 0, 24 and 48 h of incubation preserved at 37 ºC. The values obtained in control group proved that there was consumption of glucose by microorganisms after 24 and 48 h of incubation in both phases of the study. However, among experimental groups no significant differences have been observed. We conclude that the propolis 11%, 20% and 30% solutions showed the same antimicrobial action. As a result, it is justified to recommend the use of the 11% concentration. It was concluded that propolis had similar pharmacological effect when compared to the industrialized oral antiseptics tested.
Propolis; bee; saliva; microorganisms; metabolism