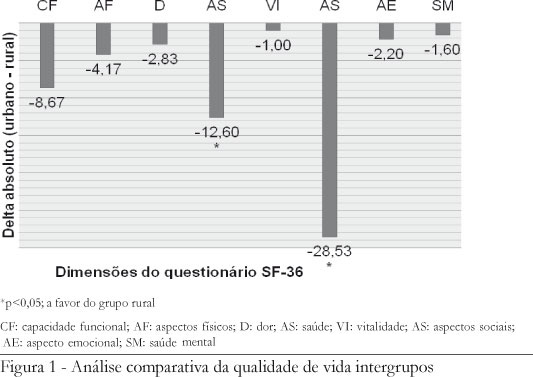
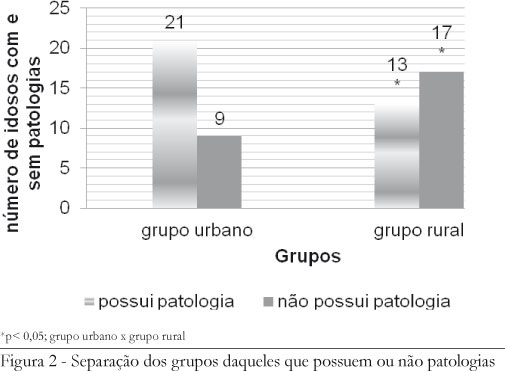
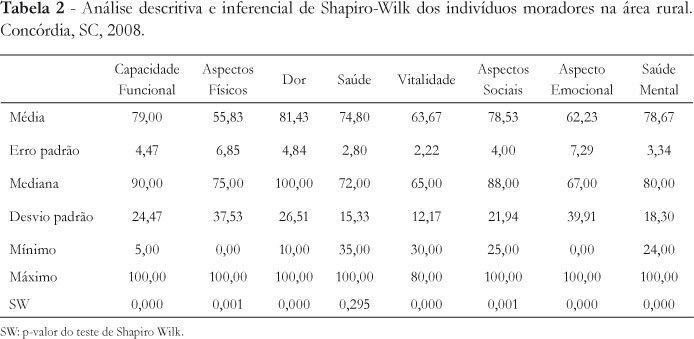
The study aimed to analyze the quality of life (QOL) among elderly people in urban and rural areas, assessing the influence of two factors (area of residence and presence or absence of pathology). The research design of epidemiological cross-sectional was conducted with elderly people (men) living in the urban and rural municipality of Concordia, SC. The sample consisted of 60 elderly people: group of the urban area (UG, n = 30, age = 68 ± 8 years) and rural (RG, n = 30, age: 67 ± 7.88 years). QOL data were collected through the Medical Outcomes Study Questionnaire Form Health Survey (SF 36). The results showed that only health (Δ = 12.60, p <0.0001) and social (Δ = 28.53, p <0.0001) variables had significant difference (p <0.05) between groups and the values of RG higher (more favorable) to the UG. The chi-square revealed a significant difference (χ2: 4.34, p = 0.037) between groups, with the RG group that has a smaller quantity of individuals with disease. Thus, it is inferred that in our sample, the RG obtained improvement in quality of life in relation to health and social aspects when compared to the UG.
Aged; Urban Population; Rural Population; Quality of Life; Concordia City